Ultimate Guide To Space Force Mos Now

Exploring the Diverse Career Opportunities in the Space Force

The United States Space Force, established in 2019, is a relatively new branch of the military with a unique focus on space operations and warfare. With its specialized mission, the Space Force offers a wide range of career paths known as Military Occupational Specialties (MOS) or Space Force Occupational Specialties (SFOS). In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various MOS options, providing an in-depth look at the roles, responsibilities, and requirements for each. Whether you’re considering a career in the Space Force or simply curious about the diverse opportunities it presents, this guide will serve as your ultimate resource.
Space Operations Officers (13S)
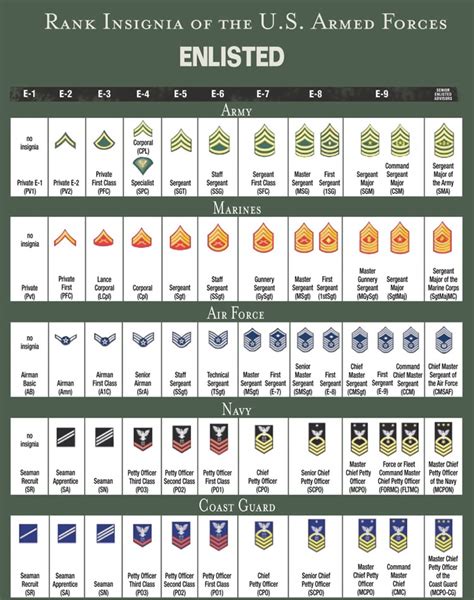
Space Operations Officers are at the forefront of the Space Force’s mission, responsible for overseeing and managing space systems and operations. Their primary role is to ensure the effective utilization of space-based assets for national security purposes. Here’s an overview of their key responsibilities:
- Space System Operations: Officers in this MOS are involved in the day-to-day management and operation of space systems, including satellites and ground-based control centers. They ensure the accurate collection and dissemination of data for intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance missions.
- Mission Planning and Execution: Space Operations Officers play a crucial role in planning and executing space-based missions. This involves analyzing mission requirements, developing operational plans, and coordinating with other military branches and government agencies.
- Space Situational Awareness: Maintaining awareness of the space environment is vital for national security. These officers monitor and analyze space weather, orbital debris, and potential threats to ensure the safety and functionality of space assets.
- Space Force Policy and Strategy: They contribute to the development of space force policies, strategies, and doctrine, shaping the future of space operations and warfare.
Intelligence Officers (14N)

Intelligence Officers in the Space Force are integral to the collection, analysis, and dissemination of intelligence information related to space operations. They play a crucial role in providing critical insights and recommendations to support decision-making at various levels. Here’s an insight into their key responsibilities:
- Intelligence Analysis: Intelligence Officers analyze a wide range of data sources, including satellite imagery, signals intelligence, and open-source information. They interpret and assess this data to identify patterns, trends, and potential threats.
- Intelligence Briefings: These officers prepare and deliver intelligence briefings to military leaders, policymakers, and other stakeholders. They ensure that decision-makers have access to the latest and most relevant intelligence information.
- Counterintelligence: Intelligence Officers also play a role in counterintelligence activities, working to identify and mitigate potential threats to the Space Force’s operations and assets.
- Intelligence Collection Management: They oversee the collection of intelligence data, ensuring that it is gathered in a lawful and ethical manner while meeting the requirements of various missions.
Cyberspace Operations Officers (17C)

Cyberspace Operations Officers are responsible for the Space Force’s cyber operations, focusing on the protection and exploitation of space-based assets in the cyber domain. Their role is critical in maintaining the security and integrity of space systems and networks. Here’s a glimpse into their key responsibilities:
- Cybersecurity: Officers in this MOS implement and oversee cybersecurity measures to protect space systems from cyber threats and attacks. They develop and maintain security protocols, monitor network activity, and respond to cyber incidents.
- Cyber Warfare: Cyberspace Operations Officers engage in offensive and defensive cyber operations, targeting adversary networks and systems to disrupt their capabilities. They employ various techniques, including hacking, network infiltration, and information warfare.
- Cyber Intelligence: These officers collect and analyze cyber intelligence, gathering information on potential threats and vulnerabilities in the cyber domain. They contribute to the development of cyber strategies and plans.
- Cyber Training and Education: Cyberspace Operations Officers are involved in training and educating Space Force personnel on cyber awareness, security practices, and defensive measures.
Missile Warning and Space Control Officers (13M)

Missile Warning and Space Control Officers are vital to the Space Force’s mission of detecting and tracking potential missile threats and maintaining space control. They play a critical role in ensuring the early detection of missile launches and the protection of space-based assets. Here’s an overview of their key responsibilities:
- Missile Warning: Officers in this MOS are responsible for monitoring and detecting missile launches, providing early warning to military and civilian authorities. They utilize advanced radar systems and satellite technology to track missile trajectories.
- Space Control: Missile Warning and Space Control Officers work to ensure the freedom of space operations and prevent interference or disruption. They implement measures to protect space-based assets from potential threats, such as hostile satellites or space debris.
- Space Surveillance: These officers maintain awareness of the space environment, tracking and cataloging objects in orbit. They contribute to the Space Force’s space situational awareness efforts, identifying potential risks and threats.
- Missile Defense: Missile Warning and Space Control Officers also play a role in missile defense operations, working with other military branches to intercept and destroy incoming missiles.
Space Systems Acquisition Officers (15F)

Space Systems Acquisition Officers are involved in the acquisition and management of space systems and technologies. They play a crucial role in ensuring that the Space Force has access to the latest and most advanced space capabilities. Here’s an insight into their key responsibilities:
- Space System Acquisition: Officers in this MOS oversee the acquisition process for space systems, including satellites, ground stations, and related technologies. They work closely with contractors and industry partners to ensure timely and effective delivery of space capabilities.
- Program Management: Space Systems Acquisition Officers manage space system programs, overseeing budgets, schedules, and performance. They ensure that projects meet technical requirements and deliver the desired capabilities.
- Contract Management: These officers are responsible for managing contracts with industry partners, negotiating terms, and ensuring compliance with regulations and specifications.
- Space System Testing and Evaluation: Space Systems Acquisition Officers oversee the testing and evaluation of space systems, ensuring they meet performance standards and operational requirements.
Launch and Range Operations Officers (13L)

Launch and Range Operations Officers are responsible for overseeing the launch and recovery of space vehicles, ensuring the successful deployment of satellites and other space assets. Their role is critical in the Space Force’s mission to maintain space superiority. Here’s an overview of their key responsibilities:
- Launch Operations: Officers in this MOS manage the launch of space vehicles, overseeing pre-launch preparations, launch procedures, and post-launch activities. They ensure the safe and successful deployment of satellites and other payloads.
- Range Operations: Launch and Range Operations Officers are responsible for the management and operation of launch ranges, including tracking and monitoring space vehicles during launch and flight. They ensure the safety and efficiency of launch operations.
- Mission Support: These officers provide mission support to space operations, coordinating with other military branches and government agencies to ensure the successful execution of space missions.
- Launch Safety: Launch and Range Operations Officers prioritize safety during launch operations, implementing safety protocols and conducting risk assessments to minimize potential hazards.
Space Battle Management Officers (13B)

Space Battle Management Officers are responsible for the planning, coordination, and execution of space-based battles and operations. They play a crucial role in ensuring the effective utilization of space assets during military operations. Here’s an insight into their key responsibilities:
- Space Battle Planning: Officers in this MOS develop and execute space battle plans, integrating space-based assets with other military branches to achieve mission objectives. They analyze enemy capabilities and vulnerabilities to develop effective strategies.
- Space Command and Control: Space Battle Management Officers oversee the command and control of space-based assets during military operations. They ensure the seamless integration of space systems with other military platforms.
- Space Situational Awareness: These officers contribute to the Space Force’s space situational awareness efforts, providing real-time intelligence and updates on the space environment to support decision-making.
- Space Force Integration: Space Battle Management Officers work closely with other military branches to ensure the effective integration of space capabilities into joint military operations.
Space Force Enlisted Specialties

In addition to officer positions, the Space Force offers a range of enlisted specialties, providing career opportunities for those interested in serving in various technical and operational roles. Here’s an overview of some of the enlisted specialties:
- Space Systems Operations (3D0X1): Enlisted personnel in this specialty operate and maintain space systems, including satellites and ground-based control centers. They ensure the accurate transmission and reception of data for intelligence and communication purposes.
- Cyberspace Operations (3D1X2): Enlisted Cyberspace Operations specialists focus on cyber operations and security. They monitor and defend space systems against cyber threats, conduct cyber warfare operations, and provide cyber support to space missions.
- Space Intelligence (3D1X3): Space Intelligence specialists analyze intelligence data related to space operations. They interpret satellite imagery, signals intelligence, and other sources to provide critical insights for decision-making.
- Space Acquisition and Contract Management (3D1X4): Enlisted personnel in this specialty support the acquisition and management of space systems. They assist in contract administration, budget management, and the coordination of space system requirements.
- Space Vehicle Operations (3D1X5): Space Vehicle Operations specialists are involved in the launch and recovery of space vehicles. They monitor and control space vehicles during flight, ensuring their safe and successful deployment.
Requirements and Qualifications

The requirements and qualifications for each MOS in the Space Force can vary, but there are some general criteria that candidates should meet. Here’s an overview:
- Education: Most MOS positions require a minimum of a bachelor’s degree in a relevant field, such as engineering, computer science, physics, or mathematics. Some specialties may have specific degree requirements.
- Physical Fitness: Candidates must meet the Space Force’s physical fitness standards, which include passing a comprehensive fitness assessment.
- Security Clearance: A high-level security clearance is typically required for most MOS positions due to the sensitive nature of space operations and the handling of classified information.
- Medical Fitness: Candidates must be in good physical and mental health, free from any conditions that may limit their ability to perform their duties.
- Leadership and Communication Skills: Strong leadership, communication, and problem-solving skills are highly valued in the Space Force, as MOS personnel often work in collaborative and dynamic environments.
Application Process
To join the Space Force and pursue a career in one of its MOS specialties, candidates must follow a specific application process. Here’s a general overview:
- Recruiting and Enlisting: Candidates can contact a Space Force recruiter to initiate the application process. The recruiter will provide guidance and assist with the completion of the necessary forms and documentation.
- Basic Training: Upon acceptance, candidates undergo basic training, also known as Basic Military Training (BMT), where they learn the fundamentals of military life, discipline, and physical fitness.
- Technical Training: After basic training, candidates attend technical training specific to their chosen MOS. This training provides them with the skills and knowledge required for their specialty.
- Assignment: Upon completion of technical training, Space Force personnel are assigned to their first duty station, where they begin their career in their chosen MOS.
Career Progression and Opportunities
The Space Force offers a wide range of career progression and development opportunities for its personnel. Here are some key aspects:
- Promotion: Space Force personnel can advance in rank through a combination of time in service, performance, and leadership potential. Promotions provide increased responsibilities and opportunities for career growth.
- Specialty Training: The Space Force provides ongoing training and development opportunities to its personnel, allowing them to enhance their skills and knowledge in their chosen MOS. This includes advanced courses, certifications, and specialized training programs.
- Cross-Training: Space Force members have the opportunity to cross-train into different MOS specialties, expanding their skill set and increasing their versatility. This can lead to new career paths and enhanced career prospects.
- Leadership Roles: As Space Force personnel progress in their careers, they may have the opportunity to take on leadership roles, such as supervising teams, managing projects, or serving as subject matter experts.
Space Force Culture and Values
The Space Force has a unique culture and set of values that shape its identity and mission. Here are some key aspects:
- Innovation and Technology: The Space Force embraces innovation and technological advancement, seeking to leverage cutting-edge technologies to enhance its space capabilities. It fosters a culture of creativity and encourages its personnel to think outside the box.
- Collaboration and Teamwork: Collaboration is a core value in the Space Force. Personnel work closely with colleagues from various specialties and branches of the military to achieve common goals and ensure the success of space operations.
- Professionalism and Ethics: The Space Force upholds high standards of professionalism and ethical conduct. Its personnel are expected to maintain integrity, respect, and a strong sense of duty in their work and interactions.
- Diversity and Inclusion: The Space Force values diversity and strives to create an inclusive environment where individuals from all backgrounds and identities can thrive. It recognizes the importance of diverse perspectives and talents in achieving its mission.
Conclusion
The United States Space Force offers a diverse range of career opportunities, each with its own unique set of responsibilities and challenges. From space operations and intelligence to cyber operations and missile warning, the Space Force plays a vital role in ensuring national security and maintaining space superiority. Whether you’re an officer or enlisted personnel, the Space Force provides a platform for personal and professional growth, allowing individuals to contribute to the nation’s space-based capabilities and make a meaningful impact. As the Space Force continues to evolve and expand, it presents exciting opportunities for those passionate about space exploration, technology, and national defense.


