Ultimate Guide To Manifold Learning Diffusion: 10 Steps

Unveiling the Power of Manifold Learning Diffusion: A Comprehensive Guide

In the realm of machine learning and data analysis, Manifold Learning Diffusion has emerged as a powerful technique, offering a unique perspective on complex datasets. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the 10 essential steps to master Manifold Learning Diffusion, empowering you to unlock the hidden patterns and insights within your data.
Step 1: Understanding the Basics

Manifold Learning Diffusion is a non-linear dimensionality reduction technique that aims to uncover the underlying structure of high-dimensional data. It is particularly useful when dealing with datasets that exhibit complex, non-linear relationships. By projecting the data onto a lower-dimensional space, Manifold Learning Diffusion enables us to visualize and analyze patterns that might be obscured in the original high-dimensional space.
Step 2: Choosing the Right Manifold Learning Algorithm

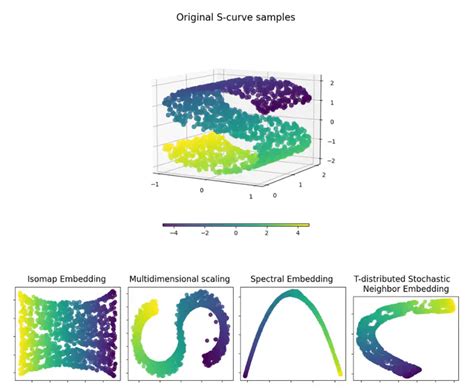
There are several manifold learning algorithms available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some popular choices include Isomap, Locally Linear Embedding (LLE), and t-distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (t-SNE). The choice of algorithm depends on the nature of your data and the specific insights you aim to uncover. Consider factors such as computational efficiency, ability to handle noise, and interpretability of the resulting embeddings.
Isomap:
- Preserves global structure well.
- Suitable for data with smooth, continuous manifolds.
LLE:
- Captures local structure effectively.
- Works well with non-linear manifolds.
t-SNE:
- Excellent for visualizing high-dimensional data.
- Preserves local structure and is effective in separating clusters.
Step 3: Preprocessing Your Data

Before applying Manifold Learning Diffusion, it's crucial to preprocess your data to ensure it's in a suitable format. This may involve normalizing the data to a common scale, handling missing values, and removing outliers that could skew the results. Additionally, consider feature scaling to ensure that no single feature dominates the analysis.
Step 4: Selecting the Target Dimension

Manifold Learning Diffusion aims to reduce the dimensionality of your data. The choice of the target dimension depends on your specific goals and the nature of your data. Generally, a lower dimension (e.g., 2D or 3D) is preferable for visualization purposes, while a higher dimension (e.g., 5D or 10D) might be necessary for more complex analyses.
Step 5: Tuning Hyperparameters

Most manifold learning algorithms have hyperparameters that control their behavior. For instance, Isomap has a k parameter that determines the number of nearest neighbors to consider, while t-SNE has perplexity and learning rate parameters. Fine-tuning these hyperparameters is crucial to achieve the best results. Experimentation and cross-validation are often necessary to find the optimal settings for your specific dataset.
Step 6: Visualizing the Results

One of the most powerful aspects of Manifold Learning Diffusion is its ability to visualize high-dimensional data in a lower-dimensional space. This visualization can reveal hidden patterns, clusters, and relationships within your data. Common visualization techniques include scatter plots, where each point represents an instance in the lower-dimensional space, and color-coding to highlight different classes or attributes.
Step 7: Evaluating the Embeddings

It's essential to evaluate the quality of the embeddings produced by Manifold Learning Diffusion. This evaluation helps ensure that the technique has accurately captured the underlying structure of your data. Common evaluation metrics include reconstruction error, which measures how well the original data can be reconstructed from the embeddings, and trustworthiness and continuity, which assess the preservation of local structure.
Step 8: Exploring Advanced Techniques

Once you've mastered the basics, you can explore more advanced techniques to enhance your Manifold Learning Diffusion analysis. These may include incorporating domain-specific knowledge to guide the embedding process, using kernel functions to capture non-linear relationships, or combining multiple embeddings to gain a more comprehensive understanding of your data.
Step 9: Integrating with Other Algorithms
Manifold Learning Diffusion can be a powerful tool when integrated with other machine learning algorithms. For example, you might use the embeddings as input to a classification or regression model, leveraging the lower-dimensional representation to improve model performance. Alternatively, you could use Manifold Learning Diffusion as a pre-processing step to reduce the dimensionality of your data before applying other dimensionality reduction techniques.
Step 10: Iterative Refinement and Interpretation
Manifold Learning Diffusion is an iterative process, and continuous refinement is key to unlocking the full potential of your data. As you explore the embeddings, you may identify new patterns or relationships that require further investigation. This iterative process of refinement and interpretation can lead to deeper insights and a more comprehensive understanding of your data.
Conclusion
Manifold Learning Diffusion is a powerful technique that empowers data analysts and machine learning practitioners to uncover hidden patterns and insights within complex datasets. By following these 10 steps, you can master Manifold Learning Diffusion and leverage its capabilities to drive data-driven decision-making and innovation. Remember, the key to success lies in understanding your data, choosing the right algorithms, and continuously refining your analysis to unlock the full potential of your data.
What is Manifold Learning Diffusion and why is it useful?
+Manifold Learning Diffusion is a non-linear dimensionality reduction technique that helps uncover the underlying structure of high-dimensional data. It is particularly useful when dealing with complex, non-linear relationships in datasets, as it allows for better visualization and analysis of patterns that might be obscured in the original high-dimensional space.
How do I choose the right Manifold Learning algorithm for my data?
+The choice of algorithm depends on the nature of your data and your specific goals. Consider factors such as computational efficiency, ability to handle noise, and interpretability of the resulting embeddings. Popular choices include Isomap, LLE, and t-SNE, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
What are some common applications of Manifold Learning Diffusion?
+Manifold Learning Diffusion is widely used in various fields, including image and signal processing, natural language processing, and bioinformatics. It can be applied to tasks such as data visualization, clustering, and feature extraction, helping to uncover hidden patterns and improve the performance of machine learning models.



