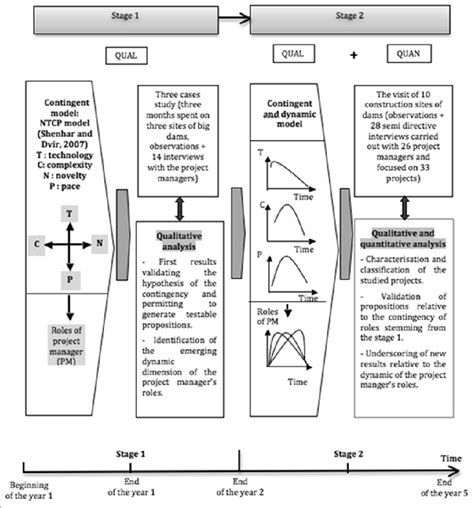
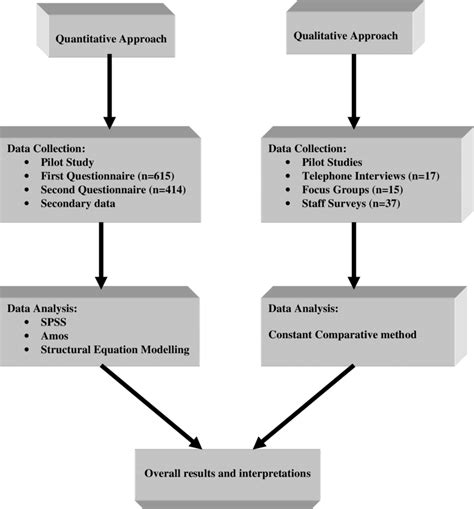
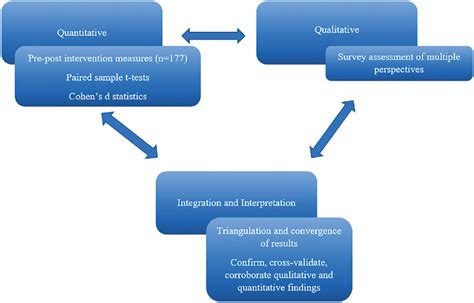
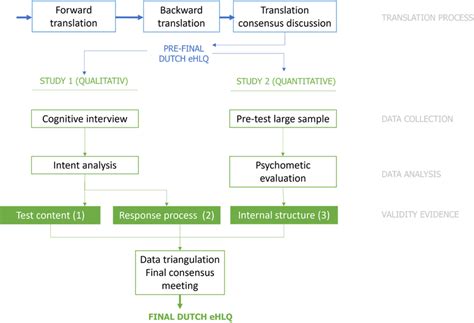
Ultimate 10Step Method To Design Concurrent Jurisdictions

Concurrent jurisdictions, also known as concurrent powers, are a fundamental concept in constitutional law and governance. It refers to the sharing of powers between different levels of government, typically between a federal or central government and state or provincial governments. Designing an effective system of concurrent jurisdictions is crucial for maintaining a balanced and efficient governance structure. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore a 10-step method to create a robust framework for concurrent jurisdictions.
Step 1: Define the Scope and Purpose
Begin by clearly defining the scope and purpose of your concurrent jurisdiction system. Identify the specific areas of governance where shared powers are necessary and the reasons behind this decision. Is it to promote local autonomy, encourage innovation, or achieve a particular policy objective? Establishing a well-defined scope will guide your design process and ensure a focused approach.
Step 2: Identify Key Areas of Governance
Identify the key areas of governance that require concurrent jurisdiction. These could include sectors such as education, healthcare, transportation, environmental protection, and economic development. Analyze the unique challenges and opportunities within each sector and determine how shared powers can address these effectively.
Step 3: Assess Existing Systems

Conduct a thorough assessment of existing concurrent jurisdiction systems, both within your country and internationally. Study successful models and learn from their strengths and weaknesses. Identify best practices and innovative approaches that can be adapted to your specific context. This step provides valuable insights and helps avoid common pitfalls.
Step 4: Determine the Level of Autonomy

Decide on the level of autonomy and decision-making authority that will be granted to each level of government. Consider factors such as the size and diversity of your country, the historical context, and the specific needs of each jurisdiction. Strike a balance between central control and local autonomy to ensure effective governance and address regional disparities.
Step 5: Establish Clear Division of Powers
Create a detailed and comprehensive division of powers between the central and state/provincial governments. Define the specific responsibilities and authorities of each level of government for each identified area of governance. Ensure that the division is clear, concise, and minimizes overlaps to prevent conflicts and promote efficient decision-making.
Step 6: Develop Mechanisms for Cooperation
Design mechanisms and institutions that facilitate cooperation and collaboration between different levels of government. Establish platforms for regular communication, information sharing, and joint decision-making. Encourage the formation of intergovernmental councils or committees to address cross-cutting issues and promote coordinated policy development.
Step 7: Define Conflict Resolution Processes
Develop robust conflict resolution processes to address disputes that may arise between different levels of government. Establish clear guidelines and protocols for handling conflicts, including mediation, arbitration, or independent dispute resolution bodies. Ensure that these processes are accessible, transparent, and fair to maintain a harmonious relationship between the central and state/provincial governments.
Step 8: Ensure Fiscal Autonomy and Accountability

Grant fiscal autonomy to state/provincial governments to enable them to raise and manage their own revenues. Establish clear guidelines for revenue sharing and fiscal transfers between the central and state/provincial governments. Promote fiscal accountability by requiring transparent budgeting, regular audits, and public reporting of financial activities.
Step 9: Promote Public Participation
Encourage public participation and engagement in the concurrent jurisdiction system. Provide opportunities for citizens to voice their opinions, concerns, and suggestions. Organize public consultations, town hall meetings, and online platforms to gather feedback and ensure that the system is responsive to the needs and aspirations of the people.
Step 10: Regular Review and Adaptation
Establish a regular review process to assess the effectiveness and efficiency of the concurrent jurisdiction system. Monitor and evaluate its performance, identify areas for improvement, and make necessary adjustments. Stay responsive to changing social, economic, and political dynamics to ensure that the system remains relevant and aligned with the needs of the population.
![]() Note: Regular review and adaptation are crucial to the long-term success of concurrent jurisdictions. Stay open to feedback and be prepared to make changes as needed.
Note: Regular review and adaptation are crucial to the long-term success of concurrent jurisdictions. Stay open to feedback and be prepared to make changes as needed.
Conclusion
Designing concurrent jurisdictions is a complex yet essential task in modern governance. By following the 10-step method outlined above, you can create a robust and balanced system that promotes local autonomy, encourages collaboration, and ensures effective decision-making. Remember to adapt the design to your specific context, continuously evaluate its performance, and be open to innovation and best practices from around the world. With a well-designed concurrent jurisdiction system, you can foster a more efficient and responsive governance structure that benefits all levels of society.
FAQ
What are the benefits of concurrent jurisdictions?
+Concurrent jurisdictions offer several advantages, including promoting local autonomy, allowing for tailored policies to meet regional needs, encouraging innovation, and fostering a more responsive governance structure.
How can conflicts between different levels of government be resolved?
+Conflicts can be resolved through well-defined dispute resolution processes, such as mediation, arbitration, or independent bodies. It is crucial to establish clear guidelines and ensure transparency and fairness in these processes.
What role does public participation play in concurrent jurisdictions?
+Public participation is vital as it ensures that the concurrent jurisdiction system is responsive to the needs and aspirations of the people. It allows citizens to have a say in the decision-making process and promotes a more inclusive and democratic governance structure.
How can fiscal autonomy be granted to state/provincial governments?
+Fiscal autonomy can be granted by allowing state/provincial governments to raise and manage their own revenues. This can be achieved through revenue-sharing agreements, fiscal transfers, and providing guidelines for transparent budgeting and financial accountability.
What are some challenges in implementing concurrent jurisdictions?
+Challenges may include balancing central control and local autonomy, managing conflicts, ensuring fiscal responsibility, and addressing regional disparities. Regular review and adaptation are key to overcoming these challenges and maintaining an effective system.


