The Essential Guide: 15 Reasons Why Fossil Fuels Reign Supreme

Introduction to Fossil Fuels

Fossil fuels have been the backbone of our energy systems for centuries, powering industrialization, economic growth, and modern life as we know it. Despite the rise of renewable energy sources, fossil fuels continue to dominate the global energy landscape. In this blog post, we will explore 15 compelling reasons why fossil fuels maintain their supremacy and remain an integral part of our energy mix. From their abundant availability to their versatility and economic benefits, we will delve into the factors that make fossil fuels an indispensable energy source.
Abundant and Accessible Reserves

One of the primary advantages of fossil fuels is their vast and easily accessible reserves. Fossil fuels, primarily coal, oil, and natural gas, are found in significant quantities worldwide. These reserves are often located in stable geological formations, making extraction relatively straightforward. The abundance of fossil fuels ensures a reliable and consistent energy supply, meeting the growing energy demands of a rapidly expanding global population.
Established Infrastructure and Technology

The dominance of fossil fuels is also attributed to the well-established infrastructure and advanced technologies that support their extraction, transportation, and utilization. Over the years, substantial investments have been made in developing efficient and sophisticated systems for the exploration, drilling, and refining of fossil fuels. This extensive infrastructure network enables the seamless distribution of fossil fuels to various sectors, including transportation, electricity generation, and industrial processes.
Reliable and Stable Energy Source

Fossil fuels provide a reliable and stable energy source, which is crucial for supporting critical infrastructure and ensuring uninterrupted power supply. Unlike intermittent renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, fossil fuels can be relied upon to generate electricity consistently, even during periods of low sunlight or calm winds. This reliability is essential for maintaining the stability and resilience of power grids and critical industries.
Proven Track Record and Performance

The extensive use of fossil fuels over centuries has led to a proven track record of performance and reliability. Fossil fuels have consistently delivered high-quality energy with predictable outcomes, making them a trusted choice for industries and consumers alike. The established technologies and processes associated with fossil fuels have been refined and optimized, resulting in efficient and cost-effective energy production.
Energy Density and Efficiency
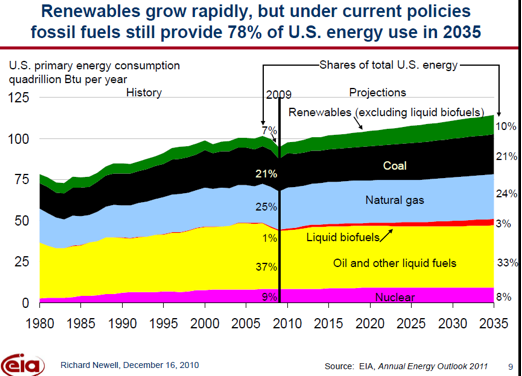
Fossil fuels are renowned for their high energy density, which means they pack a substantial amount of energy into a relatively small volume. This characteristic makes them highly efficient energy carriers, allowing for the transportation and storage of large amounts of energy over long distances. The energy density of fossil fuels enables the efficient powering of vehicles, industrial machinery, and residential appliances, contributing to the overall convenience and efficiency of modern life.
Versatility in Energy Applications

Fossil fuels offer a wide range of energy applications, making them versatile and adaptable to various sectors. They can be utilized for electricity generation, heating, transportation, and as feedstock for the production of chemicals and materials. The versatility of fossil fuels allows them to seamlessly integrate into existing energy systems, providing a flexible and reliable energy source for diverse industries and applications.
Economic Benefits and Job Creation

The fossil fuel industry plays a significant role in driving economic growth and job creation. The extraction, processing, and distribution of fossil fuels create numerous employment opportunities, both directly and indirectly. The industry supports a vast network of jobs, from exploration and drilling to refining, transportation, and power generation. Additionally, the economic benefits extend beyond job creation, as fossil fuels contribute to tax revenues, stimulate local economies, and support the development of related industries.
Energy Security and Geopolitical Stability

Fossil fuels have long been associated with energy security and geopolitical stability. The abundance of fossil fuel reserves and the well-established infrastructure for their extraction and distribution provide a sense of energy security for nations. By relying on domestic or regionally available fossil fuels, countries can reduce their dependence on volatile international markets and maintain a stable energy supply. This energy security strengthens geopolitical stability and enhances a nation’s ability to negotiate favorable energy agreements.
Cost-Effectiveness and Affordability

Fossil fuels have historically been one of the most cost-effective and affordable energy sources. The established infrastructure, efficient extraction methods, and mature supply chains have resulted in relatively low production and distribution costs. This cost-effectiveness makes fossil fuels accessible to a wide range of consumers, industries, and developing nations, ensuring energy availability and promoting economic growth.
Compatibility with Existing Infrastructure
The widespread use of fossil fuels has led to the development of extensive infrastructure tailored to their utilization. This includes power plants, refineries, pipelines, and transportation networks specifically designed for fossil fuel-based energy systems. The compatibility of fossil fuels with existing infrastructure reduces the need for costly and time-consuming retrofitting or replacement, allowing for a seamless integration of new energy sources while maintaining the reliability of the existing systems.
Energy Storage and Backup Power
Fossil fuels offer unique energy storage capabilities, providing a reliable backup power source during periods of high energy demand or disruptions in renewable energy generation. Power plants fueled by fossil fuels can quickly ramp up or down to meet sudden changes in energy requirements, ensuring a stable and consistent power supply. This flexibility in energy storage and backup power is crucial for maintaining the reliability and resilience of power grids.
Technological Advancements and Efficiency Improvements
Despite the emergence of renewable energy sources, the fossil fuel industry continues to invest in research and development, leading to significant technological advancements and efficiency improvements. Advanced extraction techniques, such as hydraulic fracturing (fracking) and horizontal drilling, have unlocked vast new reserves of oil and natural gas, enhancing the availability and sustainability of fossil fuels. Additionally, the development of cleaner burning technologies and emission reduction strategies has addressed environmental concerns associated with fossil fuel use.
Global Trade and Energy Markets
Fossil fuels play a vital role in global trade and energy markets, serving as a critical commodity for international commerce. The trade of fossil fuels, particularly oil and natural gas, facilitates economic integration and fosters diplomatic relations between nations. The global energy markets for fossil fuels are well-established and highly liquid, providing a stable and transparent platform for energy trading and price determination.
Transition to a Low-Carbon Future
While the dominance of fossil fuels is undeniable, it is important to acknowledge the need for a transition towards a low-carbon future. The environmental impact of fossil fuel combustion, particularly the emission of greenhouse gases, has led to growing concerns about climate change. However, it is worth noting that the fossil fuel industry is actively investing in research and development to mitigate these environmental impacts. Carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies, for example, have the potential to significantly reduce carbon emissions from fossil fuel-based power plants.
Conclusion
Fossil fuels continue to reign supreme due to their abundant availability, established infrastructure, reliability, and versatility. The economic benefits, energy security, and cost-effectiveness of fossil fuels make them an integral part of our energy mix. While the transition to renewable energy sources is crucial for a sustainable future, fossil fuels will likely remain a significant player in the global energy landscape for the foreseeable future. By continuing to invest in research, innovation, and environmental stewardship, we can ensure a balanced and sustainable energy transition that harnesses the strengths of both fossil fuels and renewable energy sources.
FAQ
What are the main types of fossil fuels?
+The three main types of fossil fuels are coal, oil (petroleum), and natural gas. Each of these fuels has unique characteristics and applications.
How do fossil fuels contribute to climate change?
+The combustion of fossil fuels releases greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), into the atmosphere. These gases contribute to the greenhouse effect, leading to global warming and climate change.
Are there any alternatives to fossil fuels for transportation?
+Yes, there are several alternatives to fossil fuels for transportation, including electric vehicles (EVs) powered by renewable energy sources, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, and biofuels derived from sustainable sources.
How can we reduce our dependence on fossil fuels?
+Reducing our dependence on fossil fuels requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes investing in renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, adopting sustainable transportation options, and supporting policies and initiatives that promote a transition to a low-carbon economy.
What is the future of fossil fuels in a sustainable energy landscape?
+The future of fossil fuels lies in their gradual phase-out and replacement with cleaner and more sustainable energy sources. However, it is likely that fossil fuels will continue to play a significant role in the energy mix for the foreseeable future, especially in certain sectors such as aviation and heavy industry.


