The Chemistry Of Conjugate Acids: Essential Facts

Exploring the Fundamentals of Conjugate Acids
Conjugate acids play a pivotal role in understanding the behavior of acids and bases in chemical reactions. This article delves into the chemistry of conjugate acids, offering insights into their nature, formation, and significance in various chemical processes.
What are Conjugate Acids?
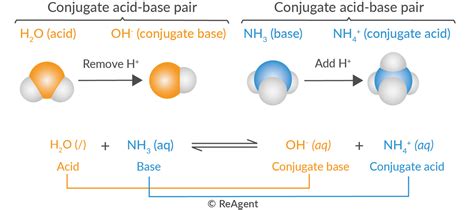
Conjugate acids are chemical species formed when a base accepts a proton (H+) during a chemical reaction. They are essentially the protonated forms of bases and are characterized by the presence of an additional hydrogen ion compared to their base counterparts.
Formation of Conjugate Acids

The formation of conjugate acids occurs through a proton transfer process. When a base accepts a proton from an acid, it transforms into its conjugate acid. This reaction is often depicted as an acid-base reaction, where the acid donates a proton and the base accepts it.
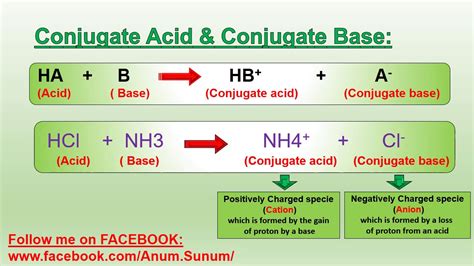
Example: Formation of Ammonium Ion (NH4+)
Consider the reaction between ammonia (NH3) and hydrochloric acid (HCl):
💡 Note: Ammonia is a weak base, while hydrochloric acid is a strong acid.
NH3 + HCl → NH4+ + Cl-
In this reaction, ammonia (NH3) accepts a proton (H+) from hydrochloric acid (HCl), forming the ammonium ion (NH4+). Ammonia acts as a base, and hydrochloric acid acts as an acid.
Properties of Conjugate Acids

Conjugate acids exhibit unique properties that distinguish them from their base counterparts:
Acidity: Conjugate acids are generally stronger acids than their corresponding bases. This is because they possess an additional hydrogen ion, making them more prone to donating protons.
Stability: The stability of a conjugate acid depends on the ability of its conjugate base to accept protons. Stronger conjugate bases can stabilize the conjugate acid by readily accepting protons.
pKa Values: The pKa value of a conjugate acid is a measure of its acidity. It represents the negative logarithm of the acid dissociation constant (Ka). A lower pKa value indicates a stronger acid.
Table: pKa Values of Some Common Conjugate Acids
| Conjugate Acid | pKa Value |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Chloride (HCl) | -6.3 |
| Ammonium Ion (NH4+) | 9.25 |
| Acetic Acid (CH3COOH) | 4.76 |
| Water (H2O) | 15.7 |

Role of Conjugate Acids in Chemical Reactions

Conjugate acids are integral to various chemical reactions, including:
Acid-Base Reactions: As mentioned earlier, conjugate acids are formed when a base accepts a proton from an acid. This process is fundamental to understanding acid-base chemistry.
Buffer Systems: Conjugate acids and their bases form buffer systems, which help maintain a relatively stable pH in solutions. Buffers resist changes in pH by accepting or donating protons as needed.
Biological Processes: Conjugate acids and bases are crucial in biological systems. For instance, the protonation and deprotonation of amino acids in proteins influence their structure and function.
Comparing Conjugate Acids and Bases

Understanding the relationship between conjugate acids and bases is essential:
Strong Acids and Weak Bases: Strong acids form weak conjugate bases, while weak acids form strong conjugate bases. This is because strong acids readily donate protons, leading to weak conjugate bases.
Weak Acids and Strong Bases: Weak acids form strong conjugate bases, while strong acids form weak conjugate bases. This relationship is based on the proton-accepting ability of the base.
Applications of Conjugate Acids

Conjugate acids find applications in various fields:
Pharmaceuticals: Understanding the behavior of conjugate acids and bases is crucial in drug design and formulation. Many drugs exist as salts, and their pH and solubility depend on the conjugate acid-base properties.
Environmental Science: Conjugate acids and bases play a role in environmental chemistry, particularly in water treatment and pollution control. Buffers are used to maintain stable pH levels in natural and industrial processes.
Food Chemistry: The acidity and alkalinity of food products are influenced by conjugate acids and bases. For example, the sour taste of citrus fruits is due to the presence of conjugate acids like citric acid.
Conclusion

Conjugate acids are a fundamental concept in chemistry, providing insights into the behavior of acids and bases. Their formation, properties, and applications make them an essential topic for anyone studying chemical reactions and their implications. Understanding conjugate acids allows scientists and researchers to predict and control chemical processes, leading to advancements in various fields.
What is the difference between a conjugate acid and a regular acid?
+
A conjugate acid is formed when a base accepts a proton, making it the protonated form of a base. Regular acids, on the other hand, are substances that can donate protons. Conjugate acids are essentially the acidic counterparts of bases.
How do conjugate acids affect the pH of a solution?
+
Conjugate acids can donate protons, which increases the concentration of H+ ions in a solution. This increase in H+ ions leads to a decrease in pH, making the solution more acidic.
What is the significance of pKa values in conjugate acids?
+
pKa values provide a measure of the acidity of a conjugate acid. A lower pKa value indicates a stronger acid, meaning it is more likely to donate protons and increase the acidity of a solution.
How do conjugate acids contribute to buffer systems?
+
Conjugate acids and their corresponding bases form buffer systems. Buffers can resist changes in pH by accepting or donating protons, maintaining a relatively stable pH in solutions.
What are some real-world applications of conjugate acids?
+
Conjugate acids are relevant in pharmaceuticals, environmental science, and food chemistry. They play a role in drug formulation, water treatment, and the acidity of food products.