Pro Guide: 7 Secrets To Perfect Ruthenium Oxide Films Now

Introduction
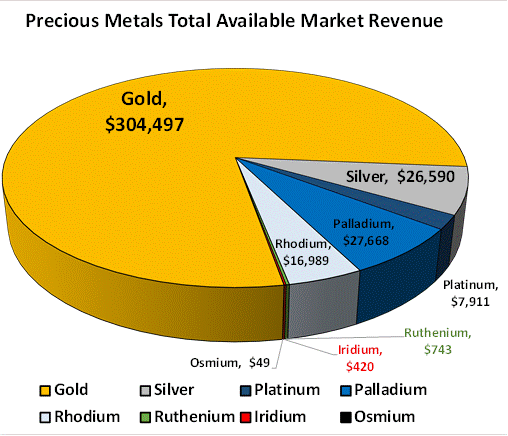
Welcome to the ultimate guide on achieving perfect ruthenium oxide films. In this comprehensive blog post, we will uncover the secrets behind creating high-quality ruthenium oxide films, a key component in various industries. By the end of this article, you will have a deep understanding of the techniques and best practices to master this intricate process. So, let’s dive in and explore the world of ruthenium oxide films!
Understanding Ruthenium Oxide Films

Ruthenium oxide films play a crucial role in numerous applications, including electronics, catalysis, and energy storage. These films offer unique properties such as high electrical conductivity, stability, and corrosion resistance. However, achieving optimal film quality requires precise control over the deposition process.
Secret 1: Choosing the Right Substrate

The first step towards perfect ruthenium oxide films is selecting an appropriate substrate. The substrate material greatly influences the film’s adhesion, morphology, and overall performance. Common substrates used for ruthenium oxide films include:
- Silicon: Silicon wafers are widely used due to their excellent compatibility with semiconductor processes.
- Glass: Glass substrates provide a smooth surface and are suitable for optical applications.
- Metal: Metals like stainless steel and titanium offer good mechanical strength and corrosion resistance.
- Flexible Substrates: For flexible electronics, materials like polyimide or polyethylene terephthalate (PET) can be considered.
Secret 2: Surface Preparation
Proper surface preparation is vital to ensure a clean and reactive surface for ruthenium oxide film deposition. Here are some key steps to follow:
- Cleaning: Begin by thoroughly cleaning the substrate to remove any contaminants. Use a suitable solvent and ultrasonic cleaning to ensure a pristine surface.
- Surface Activation: Activate the substrate surface by treating it with oxygen plasma or UV-ozone. This process enhances surface reactivity and promotes better film adhesion.
- Surface Modification: Depending on the desired film properties, surface modification techniques like self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) or chemical treatments can be employed to tailor the surface chemistry.
Secret 3: Deposition Techniques

Several deposition techniques are available for creating ruthenium oxide films. Each method offers unique advantages and considerations. Let’s explore some popular options:
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD is a widely used technique for depositing high-quality ruthenium oxide films. It involves the reaction of gaseous precursors at elevated temperatures to form the film on the substrate. Key considerations for CVD include:
- Precursor Selection: Choose suitable ruthenium-based precursors, such as ruthenium carbonyl or ruthenium chloride.
- Temperature Control: Maintain precise temperature control to ensure optimal film growth and minimize unwanted reactions.
- Gas Flow Rate: Optimize the flow rates of carrier gases and reactants to achieve the desired film thickness and uniformity.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
PVD techniques, such as sputtering and evaporation, are also employed for ruthenium oxide film deposition. These methods offer advantages like high purity and precise thickness control. Key factors to consider for PVD include:
- Target Material: Select a high-purity ruthenium target or source material.
- Vacuum Environment: Maintain a high-vacuum environment to prevent contamination and ensure efficient film deposition.
- Process Parameters: Optimize parameters like power, pressure, and substrate temperature to achieve the desired film properties.
Electrochemical Deposition
Electrochemical deposition, also known as electrodeposition or electroplating, is another method for creating ruthenium oxide films. This technique involves the reduction of ruthenium ions at the substrate surface in an electrolytic cell. Key considerations for electrochemical deposition include:
- Electrolyte Composition: Choose an appropriate electrolyte solution containing ruthenium ions.
- Current Density: Control the current density to achieve the desired film thickness and morphology.
- pH and Temperature: Maintain optimal pH and temperature conditions to promote uniform film growth.
Secret 4: Film Thickness Control
Achieving precise film thickness is crucial for optimizing the performance of ruthenium oxide films. Here are some techniques to control film thickness:
- In-Situ Monitoring: Utilize in-situ thickness monitoring tools, such as quartz crystal microbalances (QCM) or ellipsometry, to accurately measure film thickness during deposition.
- Calibration and Deposition Time: Calibrate the deposition process by correlating deposition time with film thickness. This allows for precise control over film thickness.
- Deposition Rate Adjustment: Adjust the deposition rate by modifying process parameters like precursor flow rate, power, or pressure to achieve the desired film thickness.
Secret 5: Post-Deposition Treatments

Post-deposition treatments can further enhance the properties of ruthenium oxide films. These treatments aim to improve film stability, conductivity, and overall performance. Some common post-deposition techniques include:
- Annealing: Subject the deposited film to a controlled heat treatment process. Annealing can improve film crystallinity, reduce defects, and enhance electrical conductivity.
- Surface Modification: Apply surface modification techniques, such as plasma treatment or chemical functionalization, to tailor the film’s surface properties.
- Passivation: Passivate the film to enhance its stability and corrosion resistance. This can be achieved through techniques like plasma-assisted oxidation or chemical treatments.
Secret 6: Characterization Techniques

Characterizing ruthenium oxide films is essential to understand their structural, electrical, and optical properties. Here are some commonly used characterization techniques:
- Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM): SEM provides high-resolution images of the film’s surface, allowing for the examination of morphology, grain structure, and defects.
- Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS): EDS, often coupled with SEM, analyzes the film’s elemental composition and distribution.
- X-ray Diffraction (XRD): XRD determines the crystallinity and phase composition of the film, providing insights into its structural properties.
- Raman Spectroscopy: Raman spectroscopy is useful for identifying the presence of ruthenium oxide phases and detecting any structural changes.
- Electrical Characterization: Techniques like four-point probe or Hall effect measurements can be employed to assess the film’s electrical conductivity and carrier concentration.
Secret 7: Troubleshooting and Optimization

Achieving perfect ruthenium oxide films may require troubleshooting and optimization. Here are some common issues and potential solutions:
- Non-Uniform Film Thickness: If the film thickness varies across the substrate, optimize process parameters like gas flow rates, power, or substrate rotation speed.
- Cracking or Peeling: If the film exhibits cracking or peeling, ensure proper surface preparation and consider adjusting the deposition rate or temperature.
- Poor Adhesion: To improve film adhesion, enhance surface activation techniques or explore different substrate materials.
- Impurities or Contamination: Regularly clean and maintain deposition equipment to minimize impurities. Additionally, optimize precursor purity and handling procedures.
Conclusion

Mastering the art of creating perfect ruthenium oxide films requires a deep understanding of substrate selection, surface preparation, deposition techniques, and post-deposition treatments. By following the secrets revealed in this guide, you can achieve high-quality films with optimal performance. Remember, precision and attention to detail are key to unlocking the full potential of ruthenium oxide films in your applications.
FAQ
What are the advantages of ruthenium oxide films in electronics applications?
+Ruthenium oxide films offer high electrical conductivity, stability, and resistance to oxidation, making them ideal for electronic devices. They provide excellent performance in thin-film transistors, memory devices, and energy storage systems.
Can ruthenium oxide films be deposited on flexible substrates?
+Yes, ruthenium oxide films can be deposited on flexible substrates such as polyimide or PET. This enables the development of flexible electronics, including flexible displays, wearable devices, and rollable screens.
What is the typical thickness range for ruthenium oxide films?
+The thickness of ruthenium oxide films can vary depending on the application. Typically, films range from a few nanometers to several hundred nanometers. Thicker films are often used for energy storage applications, while thinner films are suitable for electronic devices.
Are there any environmental concerns associated with ruthenium oxide film deposition?
+While ruthenium oxide film deposition is generally considered safe, it is important to handle precursors and byproducts with care. Proper ventilation and personal protective equipment should be used during the deposition process to minimize any potential health risks.
Can ruthenium oxide films be used in optical applications?
+Yes, ruthenium oxide films have optical properties that make them suitable for optical applications. They can be used as transparent conductive oxides (TCOs) in solar cells, displays, and optical coatings. Ruthenium oxide films offer high transparency and conductivity, making them an attractive alternative to traditional TCO materials.


