Lcms Technique Hcms
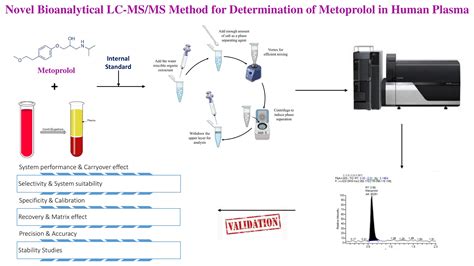
Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) is a powerful analytical technique used in various scientific fields, including chemistry, biology, and pharmacology. It combines the separation capabilities of liquid chromatography (LC) with the mass analysis provided by mass spectrometry (MS), offering a comprehensive tool for the identification and quantification of compounds.
In this blog post, we will delve into the world of LC-MS, focusing on its high-performance variant, High-Capacity Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (HCLMS or HCMs). We will explore the principles, applications, and advantages of HCLMS, as well as provide a step-by-step guide on how to perform this technique effectively.
Understanding the Basics of LC-MS

LC-MS is a hybrid technique that integrates two powerful analytical methods: liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. Liquid chromatography is employed to separate complex mixtures of compounds based on their physical and chemical properties, while mass spectrometry is used to identify and quantify these separated compounds by measuring their mass-to-charge ratios.
The combination of these two techniques allows for the analysis of a wide range of samples, from small molecules to large biomolecules, with high sensitivity and specificity. LC-MS has become an indispensable tool in various scientific disciplines due to its ability to provide detailed information about the composition and structure of complex samples.
What is High-Capacity Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (HCLMS)?

HCLMS, also known as HCMs, is an advanced version of LC-MS that offers enhanced performance and capabilities. It is designed to handle larger sample volumes and provide higher sensitivity and resolution compared to traditional LC-MS systems.
The key difference between HCLMS and conventional LC-MS lies in the chromatography system. HCLMS utilizes high-capacity columns with increased packing density and improved flow characteristics. These columns can handle higher sample loads and provide better separation efficiency, resulting in improved analytical performance.
Applications of HCLMS

HCLMS finds applications in various scientific and industrial fields, including:
- Pharmaceutical Analysis: HCLMS is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry for drug discovery, development, and quality control. It enables the identification and quantification of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), impurities, and metabolites, ensuring the safety and efficacy of medications.
- Environmental Monitoring: HCLMS plays a crucial role in environmental analysis, allowing for the detection and quantification of pollutants, pesticides, and other contaminants in water, soil, and air samples. It helps assess the impact of human activities on the environment and supports regulatory compliance.
- Food and Beverage Analysis: In the food industry, HCLMS is employed to analyze the composition and quality of food products. It aids in the detection of allergens, additives, and contaminants, ensuring consumer safety and compliance with food regulations.
- Biomedical Research: HCLMS is a valuable tool in biomedical research, particularly in proteomics and metabolomics. It enables the identification and quantification of proteins, peptides, and metabolites, providing insights into biological processes and disease mechanisms.
- Forensic Science: Forensic scientists utilize HCLMS to analyze trace evidence, such as drugs, explosives, and biological fluids. It assists in identifying and characterizing substances of interest, aiding in criminal investigations and legal proceedings.
Advantages of HCLMS

HCLMS offers several advantages over traditional LC-MS techniques, including:
- Higher Sensitivity: HCLMS provides improved sensitivity, allowing for the detection and quantification of trace amounts of compounds. This is particularly beneficial for analyzing low-concentration samples or identifying minor components in complex mixtures.
- Enhanced Resolution: The high-capacity columns used in HCLMS offer superior separation efficiency, resulting in better resolution of compounds. This enables the accurate identification and quantification of closely related compounds or isomers.
- Increased Sample Throughput: HCLMS can handle larger sample volumes and process samples more efficiently, leading to higher sample throughput. This is advantageous in high-throughput screening applications or when analyzing a large number of samples.
- Robustness and Reproducibility: The advanced chromatography system of HCLMS ensures consistent and reproducible results. The improved column packing and flow characteristics minimize variability, making it a reliable technique for quantitative analysis.
How to Perform HCLMS Analysis
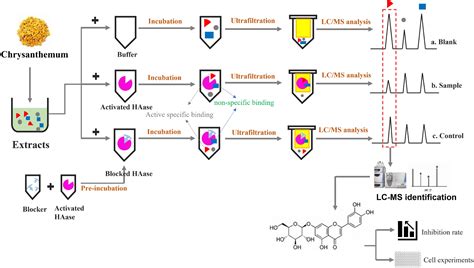
Performing HCLMS analysis involves several steps, from sample preparation to data interpretation. Here is a simplified guide to conducting an HCLMS experiment:
Step 1: Sample Preparation
- Start by collecting and preparing your sample. Ensure that the sample is appropriately stored and handled to maintain its integrity.
- If necessary, perform sample extraction or purification techniques to isolate the compounds of interest. This step may involve solid-phase extraction, liquid-liquid extraction, or other separation methods.
- Dilute or concentrate the sample to an appropriate concentration for analysis. Ensure that the sample matrix is compatible with the HCLMS system.
Step 2: Instrument Setup
- Select the appropriate HCLMS system based on your sample type and analytical goals. Consider factors such as column capacity, detector sensitivity, and mass range.
- Install the desired high-capacity column into the HCLMS system. Ensure proper connection and secure the column in place.
- Set up the mobile phase and flow rate according to the experimental conditions. Choose the appropriate solvent system and adjust the flow rate to achieve optimal separation.
- Calibrate the mass spectrometer and ensure proper alignment of the ion source and detector. This step is crucial for accurate mass measurement and data acquisition.
Step 3: Chromatographic Separation
- Inject the prepared sample into the HCLMS system. The sample will be introduced into the mobile phase, which carries it through the column.
- The compounds in the sample will interact with the stationary phase of the column, resulting in their separation based on their physicochemical properties.
- Monitor the elution of compounds using a suitable detector, such as a UV-Vis detector or a mass spectrometer. The detector provides real-time data on the presence and concentration of compounds in the sample.
Step 4: Mass Spectrometry Analysis
- Couple the HCLMS system with a mass spectrometer to perform mass analysis. The mass spectrometer ionizes the separated compounds and measures their mass-to-charge ratios.
- Acquire mass spectra for each compound eluting from the column. The mass spectra provide information on the molecular weight and structural characteristics of the compounds.
- Interpret the mass spectra to identify and quantify the compounds of interest. Utilize database search engines or reference standards to confirm the identity of the compounds.
Step 5: Data Analysis and Interpretation
- Analyze the chromatograms and mass spectra obtained from the HCLMS experiment. Use dedicated software tools to process and visualize the data.
- Quantify the compounds based on their peak areas or peak heights in the chromatograms. Calibrate the system using known standards to ensure accurate quantification.
- Interpret the results by comparing the obtained data with reference values or known compounds. Identify any anomalies or significant findings that require further investigation.
- Document and report the findings, including method validation, sample preparation details, and analytical parameters. Ensure compliance with relevant guidelines and regulations.
🌟 Note: The above steps provide a general overview of the HCLMS analysis process. It is important to consult specific protocols and guidelines for your particular HCLMS system and application.
Visualizing HCLMS Data

HCLMS generates a wealth of data, including chromatograms and mass spectra. Visualizing this data is crucial for interpreting the results and drawing meaningful conclusions. Here are some common visualizations used in HCLMS data analysis:
Chromatograms
Chromatograms are graphical representations of the separation process. They display the elution of compounds over time, with the x-axis representing time and the y-axis representing the detector response (e.g., UV absorbance or mass spectral intensity). Chromatograms provide information on the retention time, peak shape, and peak intensity of the compounds.
Mass Spectra
Mass spectra are graphical representations of the mass-to-charge ratios of ions generated from the separated compounds. They show the intensity of ions at different mass-to-charge ratios, with the x-axis representing the mass-to-charge ratio and the y-axis representing the ion intensity. Mass spectra provide valuable information on the molecular weight and structural characteristics of the compounds.
Total Ion Chromatograms (TIC)
Total ion chromatograms (TIC) are a type of chromatogram that displays the total ion current over time. It provides an overview of the entire chromatographic run, showing the overall distribution of ions across the sample. TICs are useful for identifying the presence of multiple compounds and assessing the quality of the separation.
Extracted Ion Chromatograms (EIC)
Extracted ion chromatograms (EIC) are chromatograms that focus on a specific mass-to-charge ratio of interest. By selecting a specific ion, EICs allow for the visualization of the elution profile of that particular compound. EICs are valuable for quantifying specific compounds and confirming their presence in the sample.
Troubleshooting HCLMS Analysis

While HCLMS is a powerful technique, it may encounter certain challenges or issues during analysis. Here are some common troubleshooting tips:
Poor Chromatographic Separation
- Column Condition: Ensure that the column is properly conditioned and equilibrated before use. Follow the manufacturer's guidelines for column activation and conditioning.
- Mobile Phase Composition: Review the mobile phase composition and ensure it is suitable for your sample and the compounds of interest. Adjust the solvent system if necessary.
- Flow Rate: Optimize the flow rate to achieve the desired separation efficiency. Higher flow rates may improve resolution but may also lead to peak broadening.
Low Sensitivity or Signal Interference
- Ion Source Settings: Check the ion source settings, such as ionization mode, temperature, and voltage. Adjust these parameters to optimize ionization efficiency and minimize signal interference.
- Mass Analyzer Settings: Review the mass analyzer settings, including resolution, scan range, and scan speed. Adjust these parameters to enhance sensitivity and reduce background noise.
- Matrix Effects: Consider the sample matrix and its potential impact on ionization and detection. Perform matrix-matched calibration or use internal standards to correct for matrix effects.
Mass Spectral Interference
- Sample Preparation: Ensure proper sample preparation to minimize the presence of interfering compounds. Perform extraction or purification techniques to isolate the compounds of interest.
- Mass Spectrometer Calibration: Regularly calibrate the mass spectrometer to ensure accurate mass measurement. Use appropriate calibration standards and verify the mass accuracy of the instrument.
- Isotope Pattern Analysis: Utilize isotope pattern analysis to confirm the identity of compounds. Isotope patterns can provide additional confirmation of the molecular formula and structure.
Conclusion

HCLMS is a versatile and powerful analytical technique that combines the separation capabilities of liquid chromatography with the mass analysis provided by mass spectrometry. Its high-capacity columns and advanced system design offer improved sensitivity, resolution, and sample throughput. HCLMS finds applications in various scientific fields, from pharmaceutical analysis to environmental monitoring and biomedical research.
By following the step-by-step guide and troubleshooting tips provided in this blog post, researchers and analysts can effectively perform HCLMS analysis and obtain valuable insights from their samples. HCLMS continues to evolve, with ongoing advancements in chromatography systems, mass spectrometry technologies, and data analysis software, making it an indispensable tool for modern analytical laboratories.
Frequently Asked Questions

What is the difference between LC-MS and HCLMS?
+HCLMS, or High-Capacity Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry, is an advanced version of LC-MS that utilizes high-capacity columns and improved flow characteristics. It offers higher sensitivity, resolution, and sample throughput compared to traditional LC-MS systems.
What are the advantages of HCLMS over other analytical techniques?
+HCLMS provides higher sensitivity, allowing for the detection of trace amounts of compounds. It offers enhanced resolution, enabling the accurate identification and quantification of closely related compounds. Additionally, HCLMS has increased sample throughput, making it suitable for high-throughput screening applications.
What are the common applications of HCLMS in the pharmaceutical industry?
+HCLMS is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry for drug discovery, development, and quality control. It enables the identification and quantification of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), impurities, and metabolites, ensuring the safety and efficacy of medications.
How does HCLMS contribute to environmental monitoring and analysis?
+HCLMS plays a crucial role in environmental analysis by detecting and quantifying pollutants, pesticides, and other contaminants in water, soil, and air samples. It helps assess the impact of human activities on the environment and supports regulatory compliance.
What are some tips for optimizing HCLMS analysis?
+To optimize HCLMS analysis, ensure proper sample preparation and matrix compatibility. Choose the appropriate high-capacity column and optimize the mobile phase composition and flow rate. Regularly calibrate the mass spectrometer and consider using internal standards or matrix-matched calibration to enhance accuracy and sensitivity.

