Erythrocyte Volume During Pregnancy

Pregnancy is a remarkable journey that brings about numerous physiological changes in a woman's body, and one of the key aspects affected is the circulatory system. Among the many transformations, the volume of erythrocytes, commonly known as red blood cells, plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy pregnancy. In this blog post, we will delve into the fascinating world of erythrocyte volume during pregnancy, exploring its significance, fluctuations, and impact on maternal and fetal well-being.
The Importance of Erythrocyte Volume in Pregnancy
Erythrocytes are an essential component of the blood, responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to various tissues and organs throughout the body. During pregnancy, the demand for oxygen increases significantly due to the developing fetus and the changes occurring in the mother's body. Adequate erythrocyte volume is vital to ensure sufficient oxygen supply to both the mother and the growing baby.
The placenta, a temporary organ that develops during pregnancy, plays a crucial role in facilitating the exchange of gases, nutrients, and waste products between the mother and the fetus. Erythrocytes are essential for this exchange, as they carry oxygen to the placenta, where it is transferred to the fetal circulation. This oxygen is then utilized by the fetus for growth and development, highlighting the critical role of erythrocyte volume in maintaining a healthy pregnancy.
Fluctuations in Erythrocyte Volume

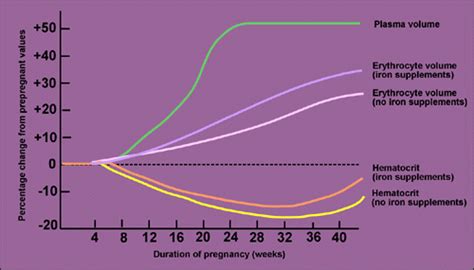
Throughout pregnancy, the volume of erythrocytes undergoes notable fluctuations. These changes are influenced by various factors, including hormonal shifts, increased blood volume, and the demands of the growing fetus.
Hormonal Influence
Pregnancy is characterized by a surge in hormonal activity, with hormones such as estrogen and progesterone playing pivotal roles. These hormones stimulate the production of erythropoietin, a hormone responsible for erythrocyte formation. As a result, the body experiences an increase in erythrocyte production, leading to a higher erythrocyte volume.
Increased Blood Volume
During pregnancy, the body undergoes a significant expansion of blood volume. On average, a pregnant woman's blood volume increases by approximately 40-50% compared to her pre-pregnancy state. This increase in blood volume is essential to support the growing fetus and meet the increased metabolic demands of pregnancy. As a result, the erythrocyte volume also rises to accommodate the expanded blood volume.
Fetal Demands
As the fetus develops and grows, its oxygen and nutrient requirements increase. The mother's body responds to these demands by adjusting the erythrocyte volume to ensure an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients to the fetus. This dynamic adaptation ensures that the fetus receives the necessary resources for optimal growth and development.
Impact on Maternal Health

The fluctuations in erythrocyte volume during pregnancy can have both positive and negative impacts on maternal health. On the positive side, the increased erythrocyte volume helps to improve oxygen delivery to the mother's tissues, reducing the risk of hypoxia and promoting overall maternal well-being.
However, certain conditions can arise that may affect maternal health. One such condition is anemia, which can occur when the body fails to produce enough erythrocytes or when there is a loss of blood. Anemia during pregnancy can lead to fatigue, weakness, and an increased risk of complications such as preterm birth and low birth weight. It is crucial for pregnant women to maintain a healthy diet rich in iron and other essential nutrients to support erythrocyte production and prevent anemia.
Impact on Fetal Development

The volume of erythrocytes during pregnancy directly influences fetal development and well-being. Adequate erythrocyte volume ensures that the fetus receives sufficient oxygen and nutrients, promoting healthy growth and organ development. Insufficient erythrocyte volume, on the other hand, can lead to fetal hypoxia, which may result in developmental delays, growth restrictions, and other adverse outcomes.
Regular prenatal care and monitoring of erythrocyte levels are essential to identify any potential issues and take appropriate measures. Healthcare providers may recommend additional tests or interventions to optimize erythrocyte volume and support fetal development.
Managing Erythrocyte Volume During Pregnancy

Maintaining a healthy erythrocyte volume during pregnancy is crucial for both maternal and fetal well-being. Here are some key strategies to support erythrocyte volume:
- Nutrition: Following a well-balanced diet rich in iron, folate, vitamin B12, and other essential nutrients is vital. Foods such as lean meats, green leafy vegetables, legumes, and fortified cereals can help meet the increased nutritional demands of pregnancy.
- Supplements: In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend iron or folic acid supplements to ensure adequate erythrocyte production and prevent deficiencies.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is essential to support blood volume expansion and maintain optimal erythrocyte volume. Drinking plenty of water and avoiding excessive caffeine intake can contribute to overall health during pregnancy.
- Regular Prenatal Care: Attending regular prenatal appointments allows healthcare providers to monitor erythrocyte levels and identify any potential concerns. Early detection and management of any issues can help ensure a healthy pregnancy outcome.
FAQs

Can anemia during pregnancy be prevented?
+Yes, anemia during pregnancy can be prevented through a combination of a healthy diet, iron supplementation (if recommended by a healthcare provider), and regular prenatal care. It is important to follow the guidance of healthcare professionals to ensure optimal erythrocyte levels.
What are the signs of low erythrocyte volume during pregnancy?
+Signs of low erythrocyte volume during pregnancy may include fatigue, weakness, pale skin, shortness of breath, and an increased heart rate. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider for further evaluation and management.
How often should erythrocyte levels be monitored during pregnancy?
+The frequency of erythrocyte level monitoring during pregnancy may vary depending on individual circumstances and the recommendations of healthcare providers. Typically, erythrocyte levels are checked at the initial prenatal visit and then periodically throughout pregnancy. However, additional tests may be ordered if there are concerns or risk factors.
Can exercise affect erythrocyte volume during pregnancy?
+Moderate exercise during pregnancy can have a positive impact on erythrocyte volume. Regular physical activity helps improve oxygen delivery to the muscles and can stimulate erythrocyte production. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine an appropriate exercise routine that aligns with individual needs and pregnancy stage.
What are the long-term effects of inadequate erythrocyte volume during pregnancy?
+Inadequate erythrocyte volume during pregnancy can have long-term effects on both the mother and the child. For the mother, it may increase the risk of postpartum anemia and fatigue. For the child, it can lead to developmental delays, growth restrictions, and an increased susceptibility to certain health conditions later in life.
Conclusion

Erythrocyte volume during pregnancy is a critical aspect of maternal and fetal health. The fluctuations in erythrocyte volume are influenced by hormonal changes, increased blood volume, and the demands of the growing fetus. By understanding the importance of erythrocyte volume and implementing strategies to support it, pregnant women can contribute to a healthy pregnancy outcome. Regular prenatal care, a nutritious diet, and staying well-hydrated are key factors in maintaining optimal erythrocyte volume and ensuring the well-being of both mother and baby.