Disposal Methods For Coal Landfilling
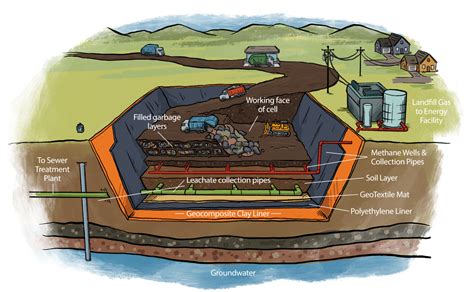
Coal, a fossil fuel, is widely used for energy generation, but its disposal can pose environmental challenges. One common method of coal disposal is landfilling, which involves burying coal waste in designated sites. However, it is crucial to explore sustainable and responsible disposal methods to minimize the environmental impact of coal waste. In this blog post, we will delve into the various disposal methods for coal landfilling, their advantages, and considerations to promote environmentally friendly practices.
Understanding Coal Landfilling

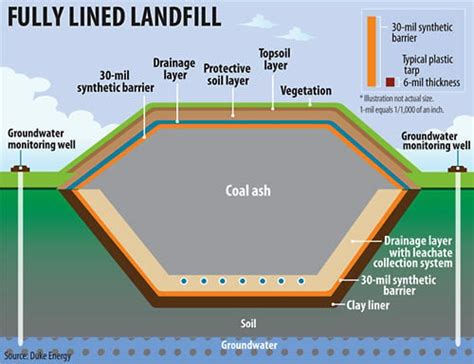
Coal landfilling is a process where coal ash, a by-product of burning coal, is disposed of in specially designed landfills. These landfills are carefully engineered to prevent the release of pollutants into the environment. While landfilling is a widely adopted practice, it is essential to explore alternative methods that can further reduce the environmental footprint of coal waste.
Alternative Disposal Methods
1. Recycling and Reuse
One of the most sustainable approaches to coal disposal is recycling and reuse. Instead of burying coal ash, it can be processed and utilized in various industries. For instance, coal ash can be used as a substitute for traditional materials in construction, such as in the production of concrete and bricks. This method not only reduces the demand for virgin resources but also minimizes the volume of waste sent to landfills.
Here are some key benefits of recycling and reusing coal ash:
- Reduced Environmental Impact: By finding alternative uses for coal ash, we can minimize the need for new resource extraction, which often has a significant environmental footprint.
- Cost-Effective: Recycling coal ash can be a cost-effective solution, as it reduces the costs associated with waste disposal and transportation.
- Resource Conservation: Utilizing coal ash in construction and other industries helps conserve natural resources, promoting a more sustainable approach to development.
2. Beneficial Use Programs
Beneficial use programs aim to promote the utilization of coal ash in a way that provides environmental and economic benefits. These programs encourage the use of coal ash in applications such as soil amendment, road construction, and landfill cover. By incorporating coal ash into these processes, we can reduce the need for traditional materials and promote a circular economy.
Consider the following advantages of beneficial use programs:
- Sustainable Development: These programs contribute to sustainable development by reducing the environmental impact of coal ash disposal and promoting resource efficiency.
- Job Creation: Implementing beneficial use programs can create job opportunities in the recycling and waste management sectors.
- Community Engagement: By involving local communities in these initiatives, we can foster a sense of environmental responsibility and encourage sustainable practices.
3. Co-Processing in Cement Kilns
Co-processing is a technique where coal ash is used as a raw material in the production of cement. Cement kilns can utilize coal ash as a substitute for traditional raw materials, reducing the need for energy-intensive extraction processes. This method not only reduces waste but also contributes to a more sustainable cement production process.
Some key advantages of co-processing in cement kilns include:
- Energy Efficiency: By using coal ash, cement kilns can reduce their energy consumption, leading to lower carbon emissions.
- Resource Optimization: Co-processing optimizes the use of resources by finding a valuable application for coal ash, which would otherwise be considered waste.
- Emission Reductions: The use of coal ash in cement production can result in lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional cement manufacturing methods.
4. Geopolymer Technology
Geopolymer technology is an innovative approach that utilizes coal ash to produce a sustainable and environmentally friendly building material. Geopolymers are inorganic polymers that can be used as an alternative to traditional cement. This technology not only reduces the environmental impact of coal ash disposal but also offers a more durable and resilient building material.
Key benefits of geopolymer technology are:
- Low Carbon Footprint: Geopolymers have a significantly lower carbon footprint compared to traditional cement, making them an eco-friendly choice.
- Durability: Geopolymer-based materials are known for their superior strength and resistance to harsh environmental conditions.
- Waste Reduction: By utilizing coal ash, geopolymer technology contributes to waste reduction and promotes a circular economy in the construction industry.
Considerations for Responsible Disposal

While exploring alternative disposal methods is crucial, it is essential to consider certain factors to ensure responsible and sustainable practices:
- Regulatory Compliance: All disposal methods must adhere to local, state, and federal regulations to prevent environmental harm.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in the decision-making process can help address concerns and promote transparency.
- Environmental Impact Assessment: Conducting thorough environmental impact assessments is vital to understand the potential effects of disposal methods on the surrounding ecosystem.
- Long-Term Monitoring: Regular monitoring of disposal sites is necessary to ensure the effectiveness of the chosen disposal method and identify any potential issues.
Implementing Sustainable Practices

To promote sustainable disposal practices, it is crucial to collaborate with industry experts, researchers, and policymakers. By sharing knowledge and best practices, we can develop innovative solutions and create a framework for responsible coal waste management.
Here are some steps to implement sustainable practices:
- Education and Awareness: Raise awareness about the environmental impact of coal waste and the benefits of sustainable disposal methods.
- Research and Development: Invest in research to explore new and improved disposal techniques that minimize environmental harm.
- Policy Support: Advocate for policies that encourage the adoption of sustainable disposal practices and provide incentives for industries to implement them.
- Collaboration: Foster collaboration between industries, academia, and government to drive innovation and find effective solutions.
Conclusion

Coal landfilling is a common practice, but by exploring alternative disposal methods, we can take a significant step towards a more sustainable future. Recycling and reusing coal ash, implementing beneficial use programs, co-processing in cement kilns, and utilizing geopolymer technology are just a few examples of how we can reduce the environmental impact of coal waste. Through responsible disposal practices and collaborative efforts, we can work towards a greener and more sustainable world.
FAQ

What is the main environmental concern associated with coal landfilling?
+The primary concern is the potential release of pollutants into the environment, including heavy metals and toxic substances, which can contaminate soil, water, and air.
How can recycling and reusing coal ash benefit the environment?
+Recycling and reusing coal ash reduces the demand for virgin resources, minimizes waste, and prevents the release of pollutants, leading to a more sustainable and eco-friendly approach.
What are the advantages of beneficial use programs for coal ash disposal?
+Beneficial use programs promote the use of coal ash in various applications, reducing waste and contributing to sustainable development while creating job opportunities.
How does co-processing in cement kilns contribute to sustainability?
+Co-processing reduces energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions, optimizes resource use, and provides an eco-friendly alternative to traditional cement production.
What makes geopolymer technology an environmentally friendly choice for construction?
+Geopolymer technology has a lower carbon footprint, produces durable materials, and utilizes coal ash, reducing waste and promoting a circular economy in construction.
