Create 6 Ultimate Vba Tips For Lowercase Checks Today

In this blog post, we will explore six valuable VBA tips focused on lowercase checks, empowering you to enhance your coding efficiency and accuracy. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced programmer, these tips will provide valuable insights to streamline your VBA journey.
1. Using the LCase Function for String Conversion
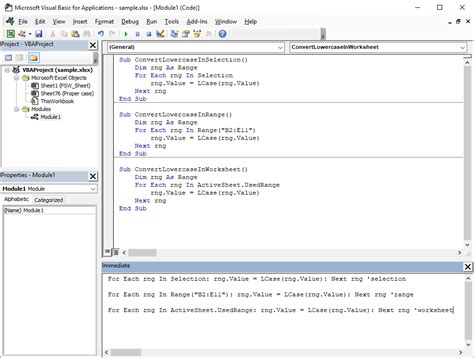
The LCase function is a powerful tool in VBA for converting strings to lowercase. It's especially useful when you need to perform case-insensitive operations or ensure uniformity in your data. Here's how you can utilize it:
Sub ConvertToLowerCase()
Dim inputString As String
Dim outputString As String
' Input a string
inputString = "Hello World!"
' Convert to lowercase
outputString = LCase(inputString)
' Display the result
MsgBox "Original: " & inputString & vbNewLine & "Lowercase: " & outputString
End Sub
This tip is a straightforward yet essential technique for data manipulation and comparison.
2. Lowercase Checks with the StrComp Function

The StrComp function is a versatile tool for string comparison, allowing you to perform case-insensitive checks. Here's an example of how to use it for lowercase comparisons:
Sub CheckLowerCase()
Dim str1 As String
Dim str2 As String
Dim result As VbCompareMethod
' Input strings
str1 = "Hello"
str2 = "hello"
' Compare and store the result
result = StrComp(str1, str2, vbTextCompare)
' Display the result
If result = 0 Then
MsgBox "The strings are equal (case-insensitive)."
Else
MsgBox "The strings are not equal."
End If
End Sub
This tip ensures accurate comparisons, regardless of the case of the input strings.
3. Automating Lowercase Conversion with Macros
VBA macros can automate the process of converting strings to lowercase. This tip is especially useful for large datasets. Here's a simple macro to achieve this:
Sub ConvertAllToLowerCase()
Dim cell As Range
' Loop through each cell in the selection
For Each cell In Selection
' Convert to lowercase
cell.Value = LCase(cell.Value)
Next cell
End Sub
By running this macro, you can quickly convert all selected cells to lowercase, saving time and effort.
4. Handling Mixed-Case Scenarios with Regular Expressions

Regular expressions offer a powerful way to handle mixed-case scenarios. Here's an example of using RegEx to match lowercase letters:
Sub MatchLowerCase()
Dim regexPattern As String
Dim inputString As String
Dim matches As Object
' Define the regular expression pattern
regexPattern = "[a-z]+"
' Input a string
inputString = "Hello World!"
' Create a regular expression object
Set matches = CreateObject("VBScript.RegExp")
matches.Pattern = regexPattern
matches.Global = True
' Find all matches
Set matches = matches.Execute(inputString)
' Display the matches
For Each match In matches
MsgBox "Match: " & match.Value
Next
End Sub
This tip demonstrates the flexibility of RegEx in VBA for complex string manipulations.
5. Custom Functions for Lowercase Checks
Creating custom functions in VBA allows you to encapsulate complex logic. Here's an example of a custom function to check if a string is entirely in lowercase:
Function IsLowerCase(inputString As String) As Boolean
Dim i As Long
' Check each character in the string
For i = 1 To Len(inputString)
' If any character is not lowercase, return False
If Asc(Mid(inputString, i, 1)) < Asc("a") Or Asc(Mid(inputString, i, 1)) > Asc("z") Then
IsLowerCase = False
Exit Function
End If
Next i
' If all characters are lowercase, return True
IsLowerCase = True
End Function
This custom function simplifies the process of validating lowercase strings.
6. Efficient Lowercase Conversion with Arrays
Arrays can significantly speed up lowercase conversions, especially with large datasets. Here's an example:
Sub ConvertWithArrays()
Dim inputArray() As String
Dim outputArray() As String
Dim i As Long
' Define input array
inputArray = Array("Hello", "World", "!")
' Allocate memory for output array
ReDim outputArray(LBound(inputArray) To UBound(inputArray))
' Convert each element to lowercase
For i = LBound(inputArray) To UBound(inputArray)
outputArray(i) = LCase(inputArray(i))
Next i
' Display the results
For i = LBound(outputArray) To UBound(outputArray)
Debug.Print outputArray(i)
Next i
End Sub
Using arrays optimizes the conversion process, making it faster and more efficient.
Conclusion

These six VBA tips for lowercase checks provide a solid foundation for handling string manipulation and comparison tasks. Whether you're converting strings, comparing them, or automating processes, these techniques will enhance your VBA coding skills. Remember to adapt these tips to your specific needs and explore further to unlock the full potential of VBA for lowercase checks and beyond.
What is the purpose of the LCase function in VBA?

+
The LCase function is used to convert a string to lowercase, ensuring uniform case representation.
How can I perform case-insensitive string comparisons in VBA?

+
The StrComp function allows for case-insensitive string comparisons, ensuring accurate results regardless of case.
What are the benefits of using arrays for lowercase conversions in VBA?

+
Arrays offer faster and more efficient lowercase conversions, especially with large datasets, optimizing performance.
Can I create custom functions for lowercase checks in VBA?

+
Absolutely! Creating custom functions in VBA allows you to encapsulate complex lowercase check logic, making your code more organized and reusable.
How can I handle mixed-case scenarios with regular expressions in VBA?
+
Regular expressions provide a powerful way to handle mixed-case scenarios, allowing you to define patterns and match specific cases.
