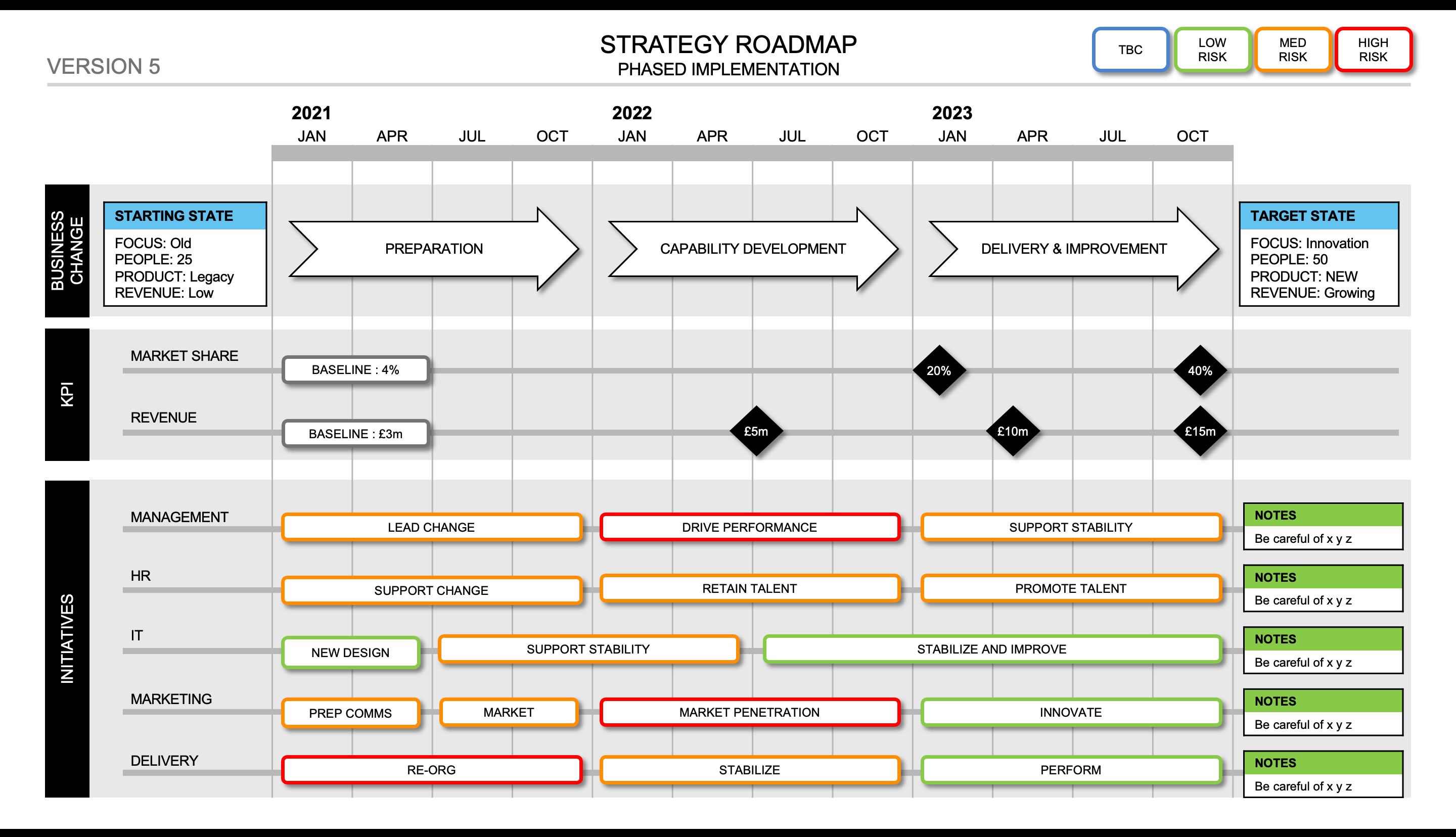
5 Pro Tips For Designing Perfect Resonance Loops Today

Introduction to Resonance Loop Design

Designing perfect resonance loops is a crucial aspect of various fields, from electronics to audio engineering. A well-designed resonance loop can enhance signal strength, improve system performance, and provide a more stable and efficient output. In this blog post, we will explore five expert tips to help you create optimal resonance loops, ensuring maximum effectiveness and precision.
Tip 1: Understand the Fundamentals
Before diving into the design process, it is essential to grasp the fundamental concepts of resonance loops. Resonance occurs when the natural frequency of a system aligns with the frequency of an external force, resulting in an amplified response. In the context of resonance loops, this amplification can be utilized to enhance specific signals or frequencies.
Key Components: - Resonant Frequency: The frequency at which resonance occurs is crucial. It determines the loop’s behavior and its interaction with external signals. - Inductors and Capacitors: These components play a vital role in creating resonance. Inductors store energy in a magnetic field, while capacitors store energy in an electric field. - Resistance: Resistance in the loop affects the overall performance and can introduce losses. Minimizing resistance is essential for efficient resonance.
Tip 2: Choose the Right Components

Selecting the appropriate components is a critical step in designing a perfect resonance loop. The choice of inductors, capacitors, and other components directly impacts the loop’s performance and stability.
Component Considerations: - Inductance and Capacitance: Select components with the desired inductance and capacitance values to achieve the target resonant frequency. - Quality Factor (Q-Factor): A higher Q-factor indicates a more efficient resonance loop. Choose components with a high Q-factor to minimize energy loss. - Tolerance: Consider the tolerance levels of the components. Tight tolerance ensures consistency and stability in the loop’s behavior.
Tip 3: Optimize Circuit Layout

The physical layout of the resonance loop circuit is crucial for minimizing interference and maximizing performance. Proper circuit design and layout techniques can significantly impact the loop’s efficiency.
Layout Tips: - Keep Traces Short: Minimize the length of traces connecting components to reduce inductance and potential interference. - Grounding: Ensure proper grounding to prevent noise and interference. Use multiple ground points and consider using a ground plane for better shielding. - Component Placement: Arrange components strategically to minimize trace lengths and reduce the risk of crosstalk. - Shielding: Consider adding shielding around sensitive components to isolate them from external interference.
Tip 4: Calibrate and Fine-Tune

Even with careful component selection and circuit layout, fine-tuning is necessary to achieve optimal performance. Calibration and adjustment are essential steps to ensure the resonance loop operates as intended.
Calibration Process: - Frequency Adjustment: Use a signal generator to sweep through the desired frequency range and identify the resonant frequency. - Component Adjustment: Fine-tune the values of inductors and capacitors to achieve the desired resonant frequency. - Test and Measure: Utilize oscilloscopes or spectrum analyzers to measure the loop’s response and ensure it meets the design specifications.
Tip 5: Consider External Factors

When designing resonance loops, it is important to consider external factors that can impact performance. Environmental conditions, nearby equipment, and electromagnetic interference can all affect the loop’s behavior.
External Factors to Consider: - Temperature: Changes in temperature can alter component values and affect the loop’s performance. Choose components with stable temperature characteristics. - Humidity: High humidity levels can impact capacitors and inductors, leading to changes in their behavior. Consider using sealed components in humid environments. - Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): Nearby equipment or power sources can generate EMI, disrupting the loop’s operation. Implement shielding and proper grounding to mitigate EMI.
Visual Representation: Resonance Loop Circuit

To better understand the concept, let’s take a look at a simplified resonance loop circuit:
| Component | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Inductor |  |
10 mH |
| Capacitor |  |
100 nF |
| Resistor |  |
100 Ω |

Conclusion

Designing perfect resonance loops requires a deep understanding of fundamental concepts, careful component selection, and precise circuit layout. By following the five expert tips outlined in this blog post, you can create resonance loops that perform optimally and efficiently. Remember to consider external factors and fine-tune your design to achieve the desired results. With these guidelines, you’ll be well on your way to mastering the art of resonance loop design.
FAQ
What is the significance of resonance in electronic circuits?
+Resonance in electronic circuits is significant as it allows for the amplification of specific frequencies or signals. This amplification can improve the performance of various systems, such as radio receivers, audio equipment, and even medical devices.
How do I calculate the resonant frequency of a resonance loop?
+The resonant frequency of a resonance loop can be calculated using the formula: f = 1 / (2π * sqrt(LC)), where f is the resonant frequency, L is the inductance, and C is the capacitance. This formula provides a basic understanding, but more complex calculations may be required for specific designs.
What are some common applications of resonance loops?
+Resonance loops find applications in various fields. They are commonly used in radio frequency (RF) circuits, audio amplifiers, filter circuits, and even in medical devices for non-invasive procedures. The ability to enhance specific frequencies makes resonance loops versatile and valuable.
Can I use resonance loops for wireless communication systems?
+Yes, resonance loops play a crucial role in wireless communication systems. They are used in antennas, filters, and amplifiers to improve signal reception and transmission. By optimizing resonance loops, wireless communication systems can achieve better range, clarity, and overall performance.
Are there any safety considerations when working with resonance loops?
+When working with resonance loops, especially at high frequencies or power levels, it is essential to consider safety precautions. This includes using proper personal protective equipment, such as gloves and eye protection, and ensuring that the work area is well-ventilated. Additionally, be cautious of potential electrical hazards and follow safety guidelines to prevent accidents.


