3. The 9 Expert Tips For Generating A Blank Unit Circle Today
Generating a Blank Unit Circle: A Comprehensive Guide

Creating a blank unit circle is an essential skill for mathematicians, engineers, and students alike. It serves as a fundamental tool for understanding trigonometry, plotting graphs, and solving complex equations. In this guide, we'll explore nine expert tips to help you generate a perfect blank unit circle effortlessly.
1. Understanding the Basics

Before we delve into the tips, let's quickly revisit the fundamentals. A unit circle is a circle with a radius of 1 unit, centered at the origin (0, 0) of a coordinate plane. It is a powerful tool for visualizing and understanding trigonometric functions, as it provides a visual representation of the relationships between angles and their corresponding coordinates on the circle.
The unit circle is particularly useful because it simplifies trigonometric calculations. By defining angles in terms of the unit circle, we can easily determine the values of trigonometric functions like sine, cosine, and tangent without the need for complex calculations. This makes it an indispensable tool for anyone working with trigonometry.
2. Choosing the Right Tools

To create a blank unit circle, you'll need the right tools. While you can certainly draw one by hand, using digital tools can save time and ensure precision. Here are some options to consider:
- Graphing Software: Programs like GeoGebra, Desmos, or Matplotlib (for Python enthusiasts) offer powerful graphing capabilities. They allow you to create custom unit circles with ease and provide options for customization.
- Online Generators: There are numerous online tools available that can generate blank unit circles for you. Simply search for "unit circle generator" and you'll find a plethora of options. These generators often provide additional features like labeling angles and coordinates.
- Vector Graphics Software: If you're comfortable with vector graphics, tools like Inkscape or Adobe Illustrator can be used to create precise and customizable unit circles.
3. Setting Up Your Workspace

Once you've chosen your tool, it's time to set up your workspace. Here are some tips to ensure a smooth process:
- Gridlines: Enable gridlines in your software to make it easier to align your unit circle accurately. Gridlines provide a visual reference, ensuring that your circle is centered and has the correct radius.
- Snap to Grid: Most software offers a "snap to grid" feature, which automatically aligns objects to the gridlines. This can be a huge time-saver and ensures precision.
- Custom Grids: If your software allows, create a custom grid with a spacing of 1 unit. This will make it easier to position your circle and mark angles accurately.
4. Drawing the Circle

Now it's time to draw the circle itself. Here's a step-by-step guide:
- Center Point: Start by creating a point at the origin (0, 0). This will be the center of your unit circle.
- Radius: Next, create a line segment with a length of 1 unit starting from the center point. This will be the radius of your circle.
- Circle Tool: Use the circle tool in your software to create a circle with the center point and radius you've just created. This will give you a perfect unit circle.
- Snap to Objects: If your software has this feature, enable it to ensure that your circle snaps to the center point and radius line, maintaining precision.
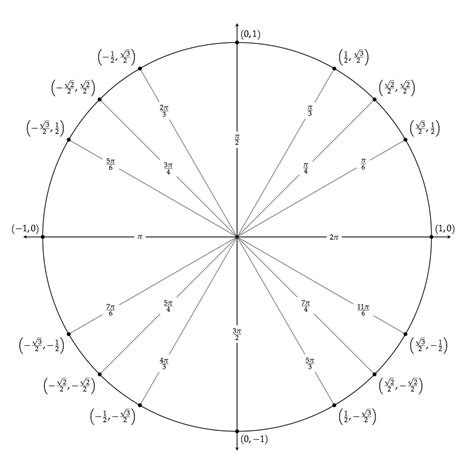
5. Labeling Angles
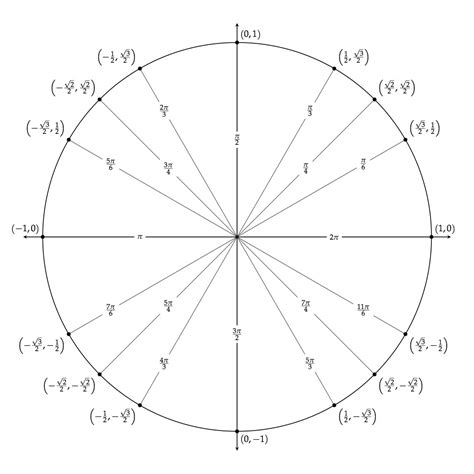
A blank unit circle is incomplete without angle labels. Here's how to add them:
- Angle Measures: Decide on the angle measures you want to include. Common choices are 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, and 90°. These angles correspond to the key trigonometric values on the unit circle.
- Create Angles: Use the angle tool in your software to create angles with the desired measures. Ensure that the angles are positioned correctly relative to the circle.
- Labeling: Add labels to each angle, indicating its measure. You can also include the corresponding trigonometric values (sine, cosine, and tangent) for each angle.
6. Customizing Your Unit Circle

Once you have the basic unit circle, you can customize it to suit your needs. Here are some ideas:
- Color Coding: Use different colors to highlight different quadrants or to distinguish between positive and negative angles.
- Dotted Lines: Add dotted lines to indicate the key angles (0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, and 90°) for a more visually appealing look.
- Grid Patterns: Experiment with different grid patterns to enhance the visual appeal of your unit circle. This can make it easier to read and understand.
7. Saving and Exporting
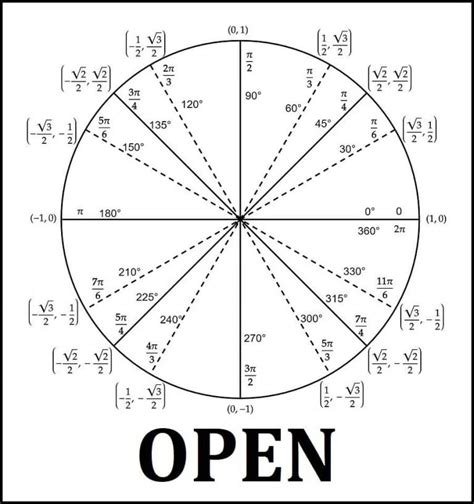
Once you're satisfied with your unit circle, it's time to save and export it. Here's how:
- Save as Image: Most software allows you to save your creation as an image file (e.g., PNG, JPEG). This is useful if you want to include your unit circle in documents or presentations.
- Vector Format: If you created your unit circle in vector graphics software, save it in a vector format like SVG. This ensures that the image remains scalable and retains its quality at any size.
- Printable Format: If you prefer a physical copy, export your unit circle as a PDF or print it directly from your software. This is especially useful for quick references or classroom use.
8. Practice and Precision

Creating a blank unit circle is a skill that improves with practice. The more you create, the easier and faster it becomes. Here are some tips to enhance your precision:
- Grid Alignment: Pay close attention to grid alignment when positioning your circle and angles. Misalignment can lead to inaccurate measurements.
- Snap Features: Utilize snap features in your software to ensure precision. These features help you align objects perfectly, reducing the risk of errors.
- Regular Practice: Practice creating unit circles regularly. The more you practice, the more comfortable you'll become with the process, leading to improved precision and speed.
9. Using Your Unit Circle
Once you've created your blank unit circle, it's time to put it to use. Here are some ideas for how to utilize it:
- Trigonometry Practice: Use your unit circle to practice calculating trigonometric values for different angles. This is an excellent way to reinforce your understanding of trigonometry.
- Graphing Functions: Plot trigonometric functions on your unit circle to visualize their behavior. This can help you understand the relationships between angles and their corresponding coordinates.
- Problem Solving: Apply your unit circle to solve complex trigonometric problems. It can serve as a visual aid, making problem-solving more intuitive and accessible.
Conclusion
Generating a blank unit circle is a valuable skill for anyone working with trigonometry or graphing. By following these expert tips, you can create precise and visually appealing unit circles with ease. Whether you're a student, educator, or professional, a well-crafted unit circle can be an invaluable tool in your mathematical toolkit. So, go ahead and give it a try! With practice, you'll master the art of creating unit circles, and your mathematical endeavors will be all the more rewarding.
What is the significance of the unit circle in trigonometry?
+The unit circle is a fundamental tool in trigonometry as it provides a visual representation of the relationships between angles and their corresponding coordinates. It simplifies trigonometric calculations and is essential for understanding trigonometric functions.
Can I create a unit circle by hand?
+Yes, you can certainly draw a unit circle by hand. However, using digital tools can save time and ensure precision, especially when creating multiple unit circles or when accuracy is crucial.
What software can I use to create a unit circle?
+There are several software options available, including graphing software like GeoGebra and Desmos, online generators, and vector graphics software like Inkscape or Adobe Illustrator.
How do I label angles on the unit circle?
+Choose the angle measures you want to include, typically 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, and 90°. Use the angle tool in your software to create angles with these measures and add labels indicating their measures and corresponding trigonometric values.
Can I customize the appearance of my unit circle?
+Absolutely! You can customize your unit circle by adding color coding, dotted lines, or different grid patterns to enhance its visual appeal and make it easier to read.
