3. Pro Tips: 5 Steps To Master Germanium's Power Today
5 Steps to Unlocking the Power of Germanium

Germanium, a versatile and fascinating element, has gained attention for its unique properties and potential applications. Whether you’re an electronics enthusiast, a health-conscious individual, or simply curious about this intriguing element, mastering Germanium’s power can open up a world of possibilities. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore five essential steps to help you harness the potential of Germanium and integrate it into your life effectively. From understanding its basic characteristics to exploring its diverse uses, we’ll cover everything you need to know to become a Germanium expert. So, let’s dive in and unlock the secrets of this remarkable element!
Step 1: Understanding the Basics
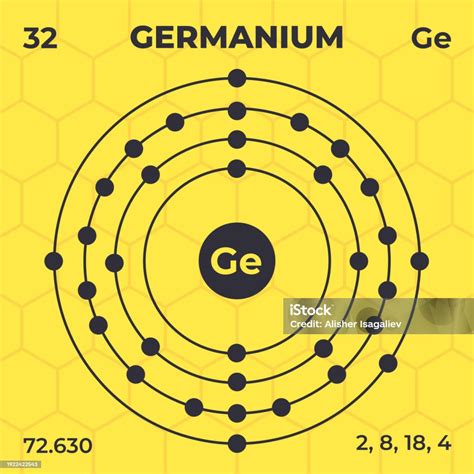
Before delving into the world of Germanium, it’s crucial to grasp its fundamental characteristics. Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It belongs to the carbon group of elements and is known for its semi-metallic properties. Here’s a quick overview:
- Chemical Properties: Germanium is a gray-white, brittle, and lustrous semiconductor. It has a high melting point and excellent thermal conductivity.
- Discovery: Germanium was first discovered in 1886 by Clemens Winkler, a German chemist. Its name is derived from the Latin word “Germania,” meaning Germany.
- Occurrence: Germanium is found in small quantities in various minerals, including argyrodite, germanite, and renierite. It is also a byproduct of zinc smelting.
- Applications: Germanium’s unique electronic properties make it an essential component in various industries. It is widely used in semiconductors, fiber optics, and infrared optics.
Step 2: Exploring Germanium’s Unique Properties
Germanium possesses several remarkable properties that set it apart from other elements. Understanding these properties is key to unlocking its full potential:
- Semiconductivity: Germanium’s ability to conduct electricity under specific conditions makes it an ideal material for semiconductor devices. It plays a crucial role in the production of diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits.
- Infrared Transparency: Germanium is highly transparent to infrared radiation, making it valuable for optical applications. It is used in infrared imaging systems, night vision devices, and heat-seeking missiles.
- Thermal Conductivity: With its excellent thermal conductivity, Germanium efficiently transfers heat. This property makes it useful in heat sinks and thermal management systems.
- Biological Significance: While Germanium is not an essential element for human health, some studies suggest potential benefits. It is believed to have antioxidant properties and may support immune function.
Step 3: Germanium in Electronics
The electronics industry heavily relies on Germanium due to its exceptional semiconductor properties. Here’s how Germanium revolutionizes the world of electronics:
- Transistors: Germanium was the first material used to create transistors, revolutionizing the electronics industry. Transistors amplify and switch electronic signals, forming the basis of modern electronic devices.
- Diodes: Germanium diodes are essential components in electronic circuits. They allow current to flow in one direction, preventing reverse current flow.
- Integrated Circuits (ICs): Germanium is a key element in the production of integrated circuits, which are the building blocks of modern computers and electronic devices. ICs integrate multiple electronic components onto a single chip.
- Optoelectronics: Germanium’s optical properties make it ideal for optoelectronic devices. It is used in lasers, photodetectors, and optical fibers, enabling high-speed data transmission.
Step 4: Germanium’s Health Benefits
While Germanium is not an essential nutrient, it has gained popularity in the health and wellness industry for its potential benefits. Here’s what you need to know:
- Antioxidant Properties: Some studies suggest that Germanium possesses antioxidant properties, helping to neutralize harmful free radicals in the body. This may contribute to overall health and well-being.
- Immune System Support: Germanium is believed to stimulate the immune system, enhancing its ability to fight off infections and diseases. It may also improve immune response in individuals with compromised immune systems.
- Pain Relief: Germanium has been studied for its potential pain-relieving properties. It is thought to have analgesic effects and may provide relief for individuals suffering from chronic pain conditions.
- Circulation Improvement: Germanium is believed to improve blood circulation, which can have positive effects on overall health. Better circulation may enhance oxygen and nutrient delivery to cells and tissues.
Step 5: Incorporating Germanium into Your Life
Now that you understand the power of Germanium, it’s time to explore practical ways to incorporate it into your daily life:
- Electronic Devices: Consider investing in high-quality electronic devices that utilize Germanium in their components. This ensures optimal performance and reliability.
- Health Supplements: If you’re interested in exploring Germanium’s potential health benefits, consult with a healthcare professional. They can guide you on the appropriate dosage and usage.
- Optical Devices: For enthusiasts interested in infrared imaging or night vision, Germanium-based optical devices can enhance your experience. These devices offer superior performance and clarity.
- Thermal Management: If you work with electronics or heat-generating devices, consider using Germanium-based heat sinks or thermal pads. They efficiently dissipate heat, preventing overheating.
Conclusion

Germanium is a versatile and powerful element with a wide range of applications. By understanding its basic characteristics, exploring its unique properties, and incorporating it into your life, you can unlock its full potential. Whether you’re an electronics enthusiast, a health-conscious individual, or simply curious, Germanium offers exciting opportunities to enhance your world. Embrace the power of Germanium and explore the endless possibilities it presents!
FAQ

What are the key applications of Germanium in the electronics industry?
+Germanium is widely used in the electronics industry for its semiconductor properties. It is a key component in transistors, diodes, integrated circuits, and optoelectronic devices. These applications have revolutionized modern electronics, making them an essential part of our daily lives.
Are there any potential health risks associated with Germanium?
+While Germanium is generally considered safe, excessive intake can lead to health issues. High doses of Germanium supplements have been linked to kidney damage and other adverse effects. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before taking Germanium supplements and to follow recommended dosages.
How does Germanium contribute to infrared imaging and night vision devices?
+Germanium’s high transparency to infrared radiation makes it an ideal material for infrared imaging and night vision devices. These devices use Germanium-based optics to capture and amplify infrared light, allowing users to see in low-light or complete darkness.
What are some common sources of Germanium in nature?
+Germanium is found in small quantities in various minerals, including argyrodite, germanite, and renierite. It is also a byproduct of zinc smelting. However, due to its limited natural occurrence, most Germanium is obtained through recycling and synthetic production.
Can Germanium be used in alternative energy applications?
+Yes, Germanium has potential applications in alternative energy technologies. Its high thermal conductivity and semiconductor properties make it suitable for use in solar cells and thermoelectric devices. These applications are being explored to enhance the efficiency and performance of renewable energy systems.
