3. Perfect Guide: How Plants Metabolize Food Now

Understanding the intricate process of how plants metabolize food is crucial for anyone interested in botany, agriculture, or even just curious about the natural world. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of plant metabolism, offering insights into the fascinating ways plants obtain and utilize nutrients for their growth and survival.
The Basics of Plant Metabolism

Plant metabolism refers to the complex biochemical processes that occur within a plant's cells, enabling it to convert raw materials, primarily sunlight, water, and nutrients from the soil, into energy and the building blocks necessary for growth, reproduction, and overall survival.
The primary process involved in plant metabolism is photosynthesis, a unique characteristic of plants that allows them to convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of glucose. This glucose serves as a fundamental energy source for the plant's metabolic activities.
Photosynthesis: The Energy-Generating Process

Photosynthesis is a multifaceted process that takes place in the chloroplasts of plant cells. It involves two main stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle.
Light-Dependent Reactions
In the light-dependent reactions, light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll and other pigments in the chloroplasts. This energy is used to split water molecules (H2O) into oxygen (O2), which is released as a byproduct, and hydrogen ions (H+). The light energy is also used to convert ADP (adenosine diphosphate) into ATP (adenosine triphosphate), a molecule that stores and transports energy within the cell.
The hydrogen ions play a crucial role in generating ATP through a process called photophosphorylation. This process occurs in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts and involves the electron transport chain, which transfers electrons from one molecule to another, ultimately leading to the formation of ATP.
Light-Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle)
The Calvin cycle, also known as the light-independent reactions, is a series of chemical reactions that take place in the stroma of the chloroplasts. It utilizes the ATP and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) produced during the light-dependent reactions to convert carbon dioxide (CO2) into glucose.
The Calvin cycle can be divided into three main stages: carbon fixation, reduction, and regeneration. During carbon fixation, CO2 is combined with a five-carbon sugar called RuBP (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate) to form a six-carbon intermediate, which then breaks down into two molecules of a three-carbon compound called 3-PGA (3-phosphoglycerate). In the reduction phase, ATP and NADPH are used to convert 3-PGA into another three-carbon sugar, G3P (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate). Finally, in the regeneration phase, some of the G3P molecules are used to regenerate RuBP, while others are used to produce glucose and other carbohydrates.
Respiration: Utilizing Energy for Growth

While photosynthesis is essential for energy production, plants also undergo a process called respiration to utilize this energy for growth and other metabolic activities. Respiration is the opposite of photosynthesis; it involves the breakdown of glucose and other carbohydrates to release energy in the form of ATP.
During respiration, glucose is oxidized in the presence of oxygen, producing carbon dioxide, water, and ATP. This process occurs in the mitochondria of plant cells and is crucial for maintaining the plant's energy levels, especially during periods of low light or when the plant is not photosynthesizing actively.
Nutrient Uptake and Transportation

In addition to sunlight and water, plants require various nutrients from the soil to support their metabolic processes. These nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and micronutrients like iron and zinc, are essential for plant growth and development.
Plants absorb these nutrients through their roots, which have specialized cells called root hairs that increase the surface area for nutrient uptake. The nutrients are then transported throughout the plant via the xylem and phloem, two distinct transport systems. The xylem primarily transports water and minerals from the roots to the leaves, while the phloem transports sugars and other organic compounds produced during photosynthesis from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
Regulation of Metabolism

Plant metabolism is a highly regulated process, with various factors influencing its efficiency and rate. Environmental factors such as light intensity, temperature, and water availability play a significant role in determining the rate of photosynthesis and respiration. Additionally, plants have evolved intricate regulatory mechanisms to optimize their metabolic processes based on their specific needs and environmental conditions.
Hormonal Regulation
Plants produce a wide range of hormones that regulate various aspects of their metabolism. For example, auxins, a class of plant hormones, play a crucial role in regulating cell growth and differentiation, while gibberellins promote stem elongation and seed germination. Cytokinins, on the other hand, stimulate cell division and delay senescence (aging) in plant tissues.
Genetic Regulation
Genetic factors also play a significant role in regulating plant metabolism. Different plant species and even different varieties within a species may have unique metabolic pathways and rates of metabolism due to variations in their genetic makeup. Additionally, plants can respond to environmental cues by altering the expression of specific genes, allowing them to adapt their metabolic processes to changing conditions.
The Role of Plant Metabolism in Agriculture
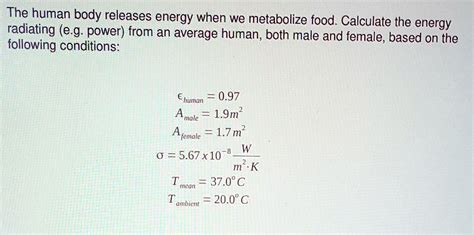
Understanding plant metabolism is not only fascinating from a scientific perspective but also has practical applications in agriculture. By manipulating and optimizing plant metabolism, farmers and scientists can improve crop yields, enhance nutrient uptake, and develop plants that are more resistant to pests and diseases.
Genetic Modification and Breeding
Genetic modification and breeding techniques allow scientists to introduce desirable traits into plants, such as increased nutrient content, improved stress tolerance, or enhanced resistance to pests and diseases. By manipulating the genetic factors that regulate plant metabolism, scientists can create crops that are better suited to specific environments and agricultural practices.
Nutrient Management
Understanding how plants metabolize nutrients is crucial for effective nutrient management in agriculture. By providing plants with the right balance of nutrients at the right time, farmers can optimize plant growth and minimize the risk of nutrient deficiencies or excesses. This knowledge also helps in the development of sustainable agricultural practices, reducing the environmental impact of farming.
Conclusion: The Significance of Plant Metabolism

Plant metabolism is a complex and fascinating process that underpins the growth, development, and survival of plants. From the intricate mechanics of photosynthesis to the regulation of metabolic pathways, plants have evolved remarkable strategies to obtain and utilize nutrients from their environment. By unraveling the mysteries of plant metabolism, we can not only deepen our understanding of the natural world but also harness this knowledge for the betterment of agriculture and the sustainability of our planet.
FAQ

What is the primary energy source for plants?
+Glucose, produced during photosynthesis, is the primary energy source for plants.
How do plants obtain nutrients from the soil?
+Plants absorb nutrients through their roots, which have specialized cells called root hairs that increase the surface area for nutrient uptake.
What is the role of hormones in plant metabolism?
+Hormones play a crucial role in regulating various aspects of plant metabolism, including cell growth, differentiation, and stress response.
How does plant metabolism impact agriculture?
+Understanding plant metabolism allows for the development of improved crop varieties, optimized nutrient management, and sustainable agricultural practices.

