2. 15+ Nucleus Ideas: Essential Guide To Remembering

Remembering and retaining information is a crucial skill, especially in today's fast-paced world where we are constantly bombarded with new knowledge and data. Whether you are a student preparing for exams, a professional aiming to enhance your memory for better performance, or simply someone looking to improve your cognitive abilities, this guide will provide you with a comprehensive set of nucleus ideas to strengthen your memory.
Understanding the Nucleus of Memory

Before we dive into the strategies, let's clarify what we mean by the "nucleus" of memory. The nucleus is the core or central part of something, and in the context of memory, it refers to the fundamental principles and techniques that form the basis of effective memory retention.
By focusing on these nucleus ideas, you can develop a strong foundation for improving your memory and making the learning process more efficient and enjoyable.
1. Association and Visualization

One of the most powerful techniques for remembering information is to create associations and visualize concepts. Our brains are wired to remember visual images and connect them to related ideas. Here's how you can utilize this:
- Create Mental Images: When learning new information, try to visualize it in your mind. For example, if you're studying the parts of a cell, imagine each component as a unique and colorful object.
- Use Associations: Connect new knowledge to something you already know. Associate it with a familiar concept, person, or place. This helps your brain form stronger connections and retrieve the information more easily.
- Mnemonic Devices: Mnemonic devices are memory aids that use associations and visualization. Acronyms, rhymes, and visual stories are popular mnemonic techniques. For instance, remember the colors of the rainbow with the acronym ROYGBIV (Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, Violet)
2. Spaced Repetition

Spaced repetition is a learning technique that involves reviewing information at increasing intervals. This method takes advantage of the spacing effect, which suggests that information is better retained when reviewed at optimal intervals.
- Create a Study Schedule: Plan your study sessions with spaced repetition in mind. Review material regularly, but increase the intervals between reviews. Start with shorter intervals and gradually increase them as you become more familiar with the content.
- Use Flashcards: Flashcards are a great tool for spaced repetition. After learning new information, create flashcards and review them at increasing intervals. You can use physical flashcards or digital apps that offer spaced repetition features.
- Digital Tools: There are various digital platforms and apps designed specifically for spaced repetition, such as Anki and Quizlet. These tools help you create digital flashcards and automatically schedule review sessions based on your progress.
3. Active Recall

Active recall is a powerful memory technique that involves actively retrieving information from your memory, rather than passively reviewing it. By engaging in active recall, you strengthen the neural pathways associated with the learned material.
- Practice Quizzing Yourself: Instead of simply re-reading your notes, quiz yourself on the material. Test your knowledge by trying to recall information without referring to your study materials.
- Use Mind Maps: Mind maps are visual diagrams that help you organize and connect ideas. Create mind maps to visualize the relationships between different concepts and actively recall information by filling in the details.
- Teach Others: One of the best ways to reinforce your understanding and memory is to teach the material to someone else. Explaining concepts to others requires active recall and helps solidify the information in your mind.
4. Elaborative Rehearsal
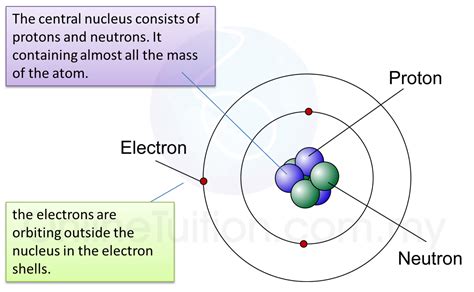
Elaborative rehearsal is a technique that involves connecting new information to existing knowledge and understanding. By elaborating on the material and making meaningful connections, you enhance your memory and comprehension.
- Relate to Prior Knowledge: When learning new concepts, actively relate them to what you already know. Look for similarities, differences, and connections between the new information and your existing knowledge base.
- Explain in Your Own Words: Try to explain the material in your own words. This forces you to process the information more deeply and understand it on a conceptual level, rather than just memorizing facts.
- Use Analogies: Analogies are powerful tools for elaborative rehearsal. Compare new concepts to familiar situations or objects to help you understand and remember them better. For example, you might compare the function of a cell's organelles to the roles of different departments in a company.
5. Contextual Learning

Contextual learning involves associating information with its context or environment. Our brains tend to remember information better when it is connected to a specific context or setting.
- Study in Different Locations: Vary your study locations. Studying in different environments helps your brain associate the material with various contexts, making it easier to recall the information later.
- Create a Study Routine: Establish a consistent study routine that includes dedicated study sessions in a specific location. Over time, your brain will associate that location with learning and retrieval of information.
- Use Real-Life Examples: Whenever possible, relate the material to real-life examples and situations. This helps you understand the practical applications of the concepts and improves your memory retention.
6. Chunking

Chunking is a memory technique that involves breaking down large amounts of information into smaller, more manageable chunks. By organizing information into meaningful groups, you can improve your memory and make it easier to recall.
- Divide and Conquer: When faced with a large amount of information, divide it into smaller sections or categories. This makes the material more digestible and helps you focus on one chunk at a time.
- Use Patterns and Groups: Look for patterns or groups within the information. For example, when learning vocabulary words, group them by theme or part of speech. This helps your brain organize and retrieve the information more efficiently.
- Create Acronyms: Acronyms are a popular chunking technique. Create acronyms by taking the first letter of each word or concept and forming a memorable word or phrase. For instance, remember the order of operations in math with the acronym PEMDAS (Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication, Division, Addition, Subtraction)
7. Interleaving
Interleaving is a learning strategy that involves mixing up different topics or concepts during study sessions. Instead of focusing on one subject at a time, interleaving allows you to switch between multiple subjects, improving your ability to discriminate and retrieve information.
- Vary Your Study Topics: Instead of studying one subject exhaustively before moving on to the next, mix up your study topics. Study a few concepts from different subjects in a single session. This helps you develop a broader understanding and improves your ability to distinguish between similar concepts.
- Practice Problem Solving: When studying math or problem-solving subjects, interleave different types of problems. Solving a variety of problems within a single session enhances your critical thinking skills and memory retrieval.
- Create Concept Maps: Concept maps are visual representations of interconnected ideas. Create concept maps that show the relationships between different subjects or topics. This helps you understand how concepts are related and improves your memory retrieval.
8. Emotionally Charged Learning
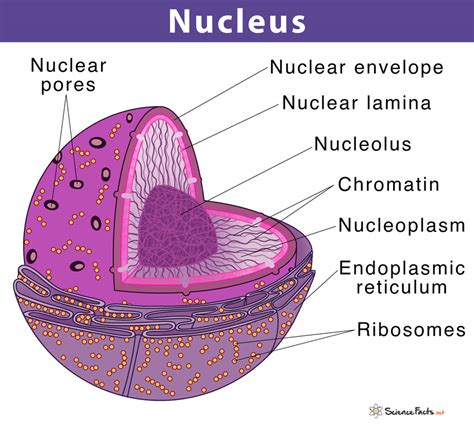
Emotions play a significant role in memory. Information that is associated with strong emotions is more likely to be remembered. You can utilize this by creating emotionally charged learning experiences.
- Engage Your Emotions: Find ways to connect emotionally with the material. If you're studying a historical event, imagine yourself as a witness or participant. Visualize the emotions and consequences of the event to create a stronger memory.
- Use Humor: Humor and laughter can enhance memory. Try to incorporate humor into your study sessions. Create funny associations or use humorous examples to make the material more memorable.
- Create Emotional Stories: When learning new concepts, create emotional stories around them. For example, if you're studying chemistry, imagine a character who discovers the properties of a particular element and how it impacts their life. This emotional story will help you remember the concept better.
9. Physical Exercise and Brain Health

Physical exercise not only benefits your body but also your brain. Regular exercise improves blood flow to the brain, promotes the growth of new neurons, and enhances cognitive function, including memory.
- Incorporate Physical Activity: Make time for regular physical exercise. Even a brisk walk or a short workout session can improve your brain's performance and memory.
- Try Brain-Boosting Exercises: Certain exercises, such as yoga and tai chi, have been shown to have positive effects on brain health and memory. These activities combine physical movement with mental focus and relaxation.
- Eat a Brain-Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in nutrients, especially omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, can support brain health and memory. Include foods like fatty fish, nuts, berries, and leafy greens in your diet.
10. Sleep and Memory Consolidation
Sleep plays a crucial role in memory consolidation. During sleep, your brain processes and organizes the information you've learned throughout the day, strengthening memory traces.
- Prioritize Sleep: Ensure you get adequate sleep each night. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep to allow your brain to consolidate memories effectively.
- Take Power Naps: Short power naps during the day can also boost your memory and cognitive performance. A 20-30 minute nap can help refresh your mind and improve memory retention.
- Avoid Sleep Deprivation: Chronic sleep deprivation can impair memory and cognitive function. Make sure you establish a consistent sleep schedule and prioritize rest to optimize your memory.
11. Mindfulness and Focus
Practicing mindfulness and improving your focus can have a significant impact on your memory and learning abilities.
- Meditate Regularly: Incorporate meditation into your daily routine. Meditation helps calm your mind, improves focus, and enhances your ability to concentrate, which is essential for effective learning and memory retention.
- Minimize Distractions: Create a study environment that minimizes distractions. Turn off notifications, find a quiet space, and focus solely on the task at hand. Undivided attention improves your memory and comprehension.
- Practice Active Listening: Whether you're in a lecture or a conversation, practice active listening. Pay attention to the speaker, ask questions, and engage with the material. Active listening improves information retention and understanding.
12. Social Learning and Collaboration
Learning and studying with others can be a powerful way to enhance your memory and understanding.
- Study Groups: Join or form study groups with peers. Discussing concepts and teaching each other can deepen your understanding and improve memory retention. Explaining ideas to others also reinforces your own knowledge.
- Online Communities: Engage with online communities and forums related to your field of study. Participating in discussions and sharing ideas with others can provide new perspectives and enhance your memory of the material.
- Collaborative Projects: Work on collaborative projects or assignments with classmates. Collaborating on a project allows you to learn from others, share ideas, and develop a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
13. Retrieval Practice
Retrieval practice is a powerful technique that involves actively recalling information from memory without referring to study materials.
- Practice Quizzing: Regularly quiz yourself on the material you've learned. Create practice tests or use existing ones to challenge your memory and reinforce your understanding.
- Use Retrieval Tools: Utilize retrieval tools such as flashcards or digital apps that allow you to practice retrieval. These tools provide immediate feedback and help you identify areas where you need to focus your studies.
- Test Yourself Regularly: Make retrieval practice a regular part of your study routine. Testing yourself frequently helps strengthen your memory and improves your ability to retrieve information when needed.
14. Multi-Sensory Learning
Engaging multiple senses during the learning process can enhance memory and comprehension.
- Use Visual Aids: Incorporate visual aids such as diagrams, infographics, or videos into your study materials. Visual representations can help you understand and remember concepts more effectively.
- Auditory Learning: If you're an auditory learner, utilize audio recordings, podcasts, or lectures to reinforce your understanding. Listening to information can be a powerful way to retain and recall it.
- Hands-on Experience: Whenever possible, seek hands-on experiences related to your studies. Practical, tactile learning can create stronger memory traces and improve your ability to apply concepts in real-world situations.
15. Spaced Retrieval
Spaced retrieval combines the benefits of spaced repetition and retrieval practice. It involves retrieving information at increasing intervals to strengthen memory.
- Create a Retrieval Schedule: Plan your retrieval practice sessions with spaced intervals in mind. Start with shorter intervals and gradually increase the time between retrieval attempts.
- Use Digital Tools: Digital platforms and apps that offer spaced retrieval features can be extremely helpful. These tools automatically schedule retrieval sessions based on your progress and adjust the intervals accordingly.
- Practice Retrieval Consistently: Make spaced retrieval a consistent part of your study routine. The more you practice retrieving information at increasing intervals, the stronger your memory will become.
16. The Power of Stories
Our brains are wired to remember stories. Narratives and storytelling techniques can greatly enhance memory and engagement.
- Create Storylines: When learning new information, try to create a narrative or storyline around it. Connect the concepts to a story that makes sense to you. This helps your brain remember the information in a more organized and memorable way.
- Use Storytelling in Teaching: If you're a teacher or educator, incorporate storytelling into your lessons. Presenting information as a story can make it more engaging and memorable for your students.
- Personalize the Story: Make the story relevant to your own life or experiences. Personalizing the narrative helps you connect with the material on a deeper level and improves your memory retention.
17. The Pomodoro Technique
The Pomodoro Technique is a time management method that can improve focus and productivity during study sessions.
- Set Timers: Break your study sessions into focused blocks of time, typically 25 minutes, followed by short breaks. This helps maintain your concentration and prevents mental fatigue.
- Stay Focused: During the focused blocks, avoid distractions and dedicate your full attention to the task at hand. Use this time to deeply engage with the material and practice active recall.
- Take Short Breaks: After each focused block, take a short break (typically 5-10 minutes). During the break, relax, stretch, or do something refreshing. This helps recharge your brain and improve your overall productivity.
18. The Zeigarnik Effect
The Zeigarnik Effect suggests that our brains tend to remember incomplete or interrupted tasks more vividly.
- Leave Tasks Incomplete: When studying, intentionally leave a task or concept slightly incomplete. This creates a sense of curiosity and motivates you to return to it later, enhancing memory retention.
- Create a Sense of Incompleteness: If you're creating study materials or notes, leave some sections intentionally unfinished. This will encourage you to review and complete them later, improving your memory of the material.
- Resume Incomplete Tasks: When you return to an incomplete task, your brain will be more inclined to remember the details and make connections, leading to better memory retention.
19. The Testing Effect
The testing effect refers to the phenomenon where testing yourself on material enhances memory retention.
- Self-Testing: Regularly test yourself on the material you’ve learned. Create practice tests or use existing ones to challenge your memory and understanding. Self-testing helps identify areas that need further study and reinforces your memory.

