2. 10 Powerful Germanium Emission Secrets You Need Now

In the realm of electronic components, Germanium has emerged as a powerhouse, offering a myriad of benefits and unique characteristics. This blog will delve into ten secrets of Germanium emissions, unveiling their power and potential, and providing you with valuable insights to harness their capabilities effectively.
1. The Rise of Germanium: A Historical Perspective

Germanium, a semiconductor material, has a rich history in the world of electronics. Discovered in the late 19th century, it gained prominence during the early days of radio technology. Its ability to amplify signals and conduct electricity with precision made it a sought-after material for early radios and other electronic devices. Over time, Germanium’s role evolved, and it became a key player in the development of modern electronics, especially in the era of transistor radios.
2. Unlocking Germanium’s Potential: Emission Secrets
Germanium’s true power lies in its unique emission properties. When subjected to specific conditions, Germanium emits energy in the form of light or heat, a phenomenon known as photoluminescence or thermoluminescence. This emission can be harnessed for a wide range of applications, from optical sensors to energy-efficient lighting.
3. The Science Behind Germanium Emissions

At the heart of Germanium’s emission secrets is its atomic structure. Germanium atoms have a unique arrangement of electrons, which, when excited by energy input, release photons—the fundamental particles of light. This process, known as quantum mechanics, is what gives Germanium its emission capabilities.
4. Applications of Germanium Emissions

The versatility of Germanium emissions is remarkable. Here are some key applications:
- Optoelectronics: Germanium-based optoelectronic devices, such as photodiodes and LEDs, are crucial for optical communication systems, image sensors, and laser technology.
- Energy Efficiency: Germanium’s emission properties make it an ideal material for energy-efficient lighting, reducing power consumption and environmental impact.
- Sensors and Detectors: Germanium-based sensors are highly sensitive, making them perfect for detecting and measuring light, heat, and radiation.
- Solar Cells: Germanium’s ability to absorb and convert sunlight into electricity makes it a valuable material for solar cell technology.
5. The Benefits of Germanium Emissions

Emissions from Germanium offer a plethora of advantages:
- Efficiency: Germanium-based devices are highly efficient, converting energy with minimal loss.
- Sensitivity: The sensitivity of Germanium sensors is unparalleled, making them ideal for precise measurements.
- Durability: Germanium’s stability and resistance to environmental factors ensure long-lasting performance.
- Environmental Impact: Germanium’s energy-efficient properties contribute to a greener and more sustainable future.
6. Unveiling the Power: Germanium Emission Types
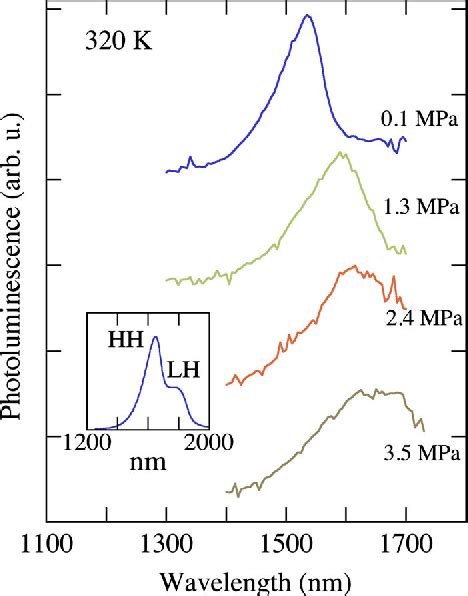
Germanium emissions can be categorized into two main types:
- Photoluminescence: This emission occurs when Germanium is exposed to light, releasing photons of a different wavelength.
- Thermoluminescence: Here, Germanium emits light or heat when exposed to an external heat source.
7. Maximizing Germanium’s Potential: Design Considerations

To harness the full power of Germanium emissions, careful design considerations are essential. Factors such as doping (adding impurities to control conductivity), device structure, and operating conditions play a crucial role in optimizing performance.
8. The Future of Germanium Emissions

The potential for Germanium emissions is vast and ever-evolving. Ongoing research and development are exploring new applications, such as:
- Quantum Computing: Germanium’s quantum properties make it a promising material for quantum computing, a technology that could revolutionize information processing.
- Medical Imaging: Germanium-based sensors and detectors could enhance medical imaging, leading to more accurate diagnoses.
- Environmental Monitoring: Germanium sensors can be used to monitor and detect environmental changes, aiding in climate research and pollution control.
9. Challenges and Opportunities
While Germanium emissions offer immense potential, there are challenges to consider. Cost and availability of Germanium can be limiting factors. However, ongoing research aims to address these challenges, making Germanium more accessible and cost-effective.
10. Practical Tips for Working with Germanium Emissions

If you’re working with Germanium emissions, here are some practical tips to consider:
- Ensure a clean and controlled environment to minimize contamination and optimize performance.
- Pay attention to temperature and humidity control, as these factors can impact Germanium’s emission properties.
- Consider safety precautions when handling Germanium, especially when working with high-energy applications.
![]() Note: Always refer to safety guidelines and regulations when working with electronic components.
Note: Always refer to safety guidelines and regulations when working with electronic components.
Conclusion
Germanium emissions are a powerful force in the world of electronics, offering a wide range of applications and benefits. From optoelectronics to energy efficiency, Germanium’s unique properties continue to shape the future of technology. By understanding and harnessing these emission secrets, we can unlock a world of possibilities, driving innovation and sustainability.
What is Germanium’s role in modern electronics?
+Germanium is a key material in modern electronics, particularly in optoelectronic devices and energy-efficient technologies.
How does Germanium’s emission work?
+Germanium’s emission is based on its atomic structure and quantum mechanics, releasing photons when excited by energy input.
What are the main benefits of Germanium emissions?
+Germanium emissions offer efficiency, sensitivity, durability, and environmental benefits, making them ideal for various applications.
Are there any challenges associated with Germanium emissions?
+Challenges include the cost and availability of Germanium, but ongoing research aims to address these issues.