15+ Ways Coal Affects Soil: A Mustsee Tutorial For Gardeners And Farmers

Coal, a fossil fuel with a dark and complex history, has long been a subject of concern due to its environmental impact. While its effects on air and water quality are well-documented, the influence of coal on soil often goes unnoticed. For gardeners and farmers, understanding how coal affects soil health is crucial for maintaining fertile and productive land.
In this tutorial, we will explore over 15 ways in which coal can impact soil, shedding light on the potential risks and offering insights into sustainable practices. By the end, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of coal's role in soil health and be equipped with the knowledge to make informed decisions for your garden or farm.
1. Soil Acidification

Coal combustion produces sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, which can lead to acid rain. When this acidic precipitation reaches the soil, it lowers the pH level, making the soil more acidic. Acidic soil can hinder plant growth and reduce nutrient availability, affecting overall soil health.
2. Nutrient Imbalance

Coal combustion also releases various heavy metals, such as mercury, lead, and cadmium, into the environment. These metals can accumulate in the soil, leading to nutrient imbalances. High levels of heavy metals can be toxic to plants and disrupt their growth, affecting the overall nutrient cycle in the soil.
3. Soil Contamination

Coal ash, a byproduct of coal combustion, contains toxic substances like arsenic, selenium, and chromium. When coal ash is improperly disposed of or spills occur, it can contaminate the soil. Contaminated soil poses risks to plant health and can lead to the accumulation of toxins in the food chain.
4. Reduced Water Holding Capacity

Soil contaminated with coal ash or other coal byproducts may have reduced water-holding capacity. This can result in drier soil conditions, making it challenging for plants to access adequate moisture, especially during dry periods.
5. Soil Structure Degradation
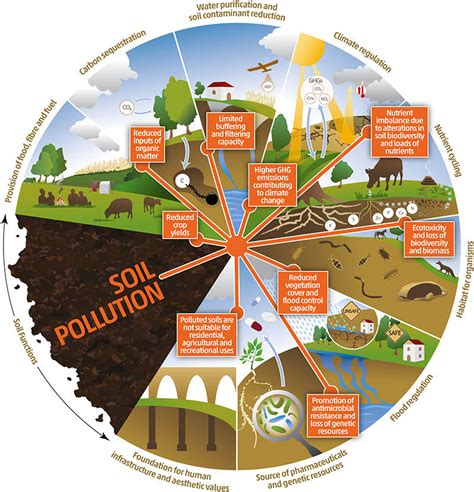
Coal mining activities can lead to soil compaction and degradation of soil structure. Heavy machinery and the removal of topsoil can disrupt the natural soil profile, affecting water infiltration, root growth, and overall soil health.
6. Loss of Organic Matter

Coal mining and the use of coal-derived fertilizers can deplete organic matter in the soil. Organic matter is crucial for soil fertility, as it improves soil structure, enhances water-holding capacity, and provides essential nutrients for plant growth.
7. Soil Erosion

Soil erosion is a significant concern in areas where coal mining takes place. The removal of vegetation and topsoil, combined with the exposure of bare soil, can lead to increased erosion rates. Eroded soil not only affects the quality of nearby water bodies but also reduces the productivity of the land.
8. Impact on Microbial Activity

Soil is teeming with microorganisms that play a vital role in nutrient cycling and plant health. Coal and its byproducts can disrupt the balance of these microbial communities, affecting their ability to break down organic matter and release nutrients for plant uptake.
9. Heavy Metal Uptake by Plants

Plants growing in soil contaminated with heavy metals from coal combustion may absorb these metals through their roots. This can lead to the accumulation of toxins in plant tissues, making them unsafe for consumption by humans and animals.
10. Reduced Seed Germination

Soil contaminated with coal byproducts or heavy metals can inhibit seed germination. This can result in reduced crop yields and affect the overall productivity of agricultural lands.
11. Impact on Beneficial Insects
Soil health is closely linked to the presence of beneficial insects, such as earthworms and beetles. Coal mining and the use of coal-derived pesticides can negatively impact these insects, disrupting the natural balance of the ecosystem and affecting soil fertility.
12. Soil Salinity
Coal mining activities can increase soil salinity, especially in arid regions. High salt concentrations in the soil can hinder plant growth and reduce water availability, leading to decreased crop yields.
13. Air Pollution Deposition
Air pollution from coal-fired power plants can deposit pollutants onto the soil surface. These pollutants, including heavy metals and toxic chemicals, can contaminate the soil and affect its quality.
14. Impact on Soil Enzymes
Soil enzymes are essential for various biochemical processes in the soil. Coal and its byproducts can inhibit the activity of these enzymes, disrupting nutrient cycling and soil health.
15. Altered Soil pH
As mentioned earlier, coal combustion can lead to acid rain, which can alter the pH of the soil. This change in pH can affect the availability of nutrients and the overall health of the soil ecosystem.
16. Impact on Soil Biodiversity
Soil biodiversity, including microorganisms, insects, and other soil-dwelling organisms, is crucial for maintaining soil health. Coal mining and the use of coal-derived products can disrupt this biodiversity, affecting the overall balance and function of the soil ecosystem.
17. Increased Risk of Soil-Borne Diseases
Soil contaminated with coal byproducts or heavy metals can create an environment conducive to the growth of soil-borne pathogens. This can increase the risk of plant diseases and affect crop health.
18. Long-Term Effects on Soil Fertility
The cumulative impact of coal on soil can have long-term effects on soil fertility. Over time, the depletion of organic matter, nutrient imbalances, and soil contamination can lead to a decline in soil quality and productivity.
Sustainable Practices for Soil Health
While the impact of coal on soil is concerning, there are sustainable practices that gardeners and farmers can adopt to mitigate these effects and promote soil health.
1. Soil Testing
Regular soil testing can help identify potential issues caused by coal or its byproducts. This allows for targeted interventions and the implementation of appropriate soil management practices.
2. Cover Crops and Green Manure
Planting cover crops and using green manure can help improve soil health by adding organic matter, enhancing soil structure, and promoting nutrient cycling.
3. Composting
Composting is an effective way to recycle organic waste and improve soil fertility. Compost adds essential nutrients and beneficial microorganisms to the soil, enhancing its overall health.
4. Crop Rotation
Implementing crop rotation can help break pest and disease cycles, improve soil structure, and optimize nutrient use. Rotating crops can also help reduce the accumulation of heavy metals in the soil.
5. Conservation Tillage
Conservation tillage practices, such as no-till or reduced tillage, can help minimize soil disturbance and preserve soil structure. These practices also help prevent soil erosion and maintain soil organic matter.
6. Integrated Pest Management
Adopting integrated pest management (IPM) strategies can reduce the reliance on coal-derived pesticides. IPM focuses on using a combination of cultural, biological, and chemical methods to manage pests, minimizing the impact on soil health.
7. Water Management
Efficient water management practices, such as drip irrigation and water-saving techniques, can help reduce the impact of coal on soil moisture levels. Proper water management can also help prevent water contamination from coal ash or other byproducts.
8. Soil Conservation Measures
Implementing soil conservation measures, such as terracing, contour farming, and windbreaks, can help prevent soil erosion and maintain soil health in areas affected by coal mining or combustion.
9. Education and Awareness
Raising awareness about the impact of coal on soil health is crucial. Educating farmers, gardeners, and the general public about sustainable practices can lead to collective efforts to protect and restore soil health.
Conclusion
The impact of coal on soil is multifaceted and can have far-reaching consequences for gardeners, farmers, and the environment. By understanding the various ways coal affects soil health, we can make informed decisions and adopt sustainable practices to mitigate these effects. Through soil testing, conservation measures, and the adoption of eco-friendly farming techniques, we can work towards preserving and enhancing the fertility of our soils for future generations.
What are the long-term effects of coal on soil fertility?
+The long-term effects of coal on soil fertility include the depletion of organic matter, nutrient imbalances, and soil contamination. These factors can lead to a decline in soil quality and productivity over time.
How can gardeners and farmers mitigate the impact of coal on soil health?
+Gardeners and farmers can mitigate the impact of coal on soil health by adopting sustainable practices such as soil testing, cover cropping, composting, crop rotation, conservation tillage, integrated pest management, and water management. These practices help improve soil health, fertility, and productivity.
What are the main sources of coal pollution in soil?
+The main sources of coal pollution in soil include coal combustion, which releases sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and heavy metals, and coal mining activities, which can lead to soil compaction, erosion, and the release of coal byproducts.
How does coal affect soil pH levels?
+Coal combustion can lead to acid rain, which lowers the pH of the soil, making it more acidic. Acidic soil can hinder plant growth and reduce nutrient availability, affecting overall soil health.
What are the potential risks of soil contaminated with coal byproducts?
+Soil contaminated with coal byproducts, such as coal ash, can pose risks to plant health and lead to the accumulation of toxins in the food chain. Contaminated soil may also have reduced water-holding capacity and altered nutrient cycling, affecting overall soil fertility.


