15+ Facts About Crop Rotation: Essential Insights For Farmers

Crop rotation is a vital practice in agriculture, offering numerous benefits to farmers and the environment. By understanding the science behind crop rotation and implementing effective strategies, farmers can enhance soil health, improve crop yields, and promote sustainable farming practices. In this blog post, we will explore over 15 essential facts about crop rotation, providing valuable insights for farmers to optimize their agricultural practices.
The Benefits of Crop Rotation

Crop rotation is an age-old technique that has stood the test of time, and for good reason. It offers a plethora of advantages, including:
- Improved soil fertility: By rotating crops, farmers can enhance soil structure, nutrient content, and organic matter, leading to healthier and more productive soil.
- Pest and disease management: Different crops attract different pests and diseases. Rotating crops can disrupt the life cycles of pests and pathogens, reducing the risk of infestations and the need for chemical interventions.
- Weed control: Certain crops are better at suppressing weeds than others. By strategically planning crop rotations, farmers can minimize weed pressure and reduce the reliance on herbicides.
- Enhanced nutrient cycling: Different crops have varying nutrient requirements and uptake patterns. Rotating crops allows for better nutrient cycling, ensuring that essential nutrients are available for subsequent crops.
- Reduced soil erosion: Crop rotation helps to protect soil from erosion by wind and water. Cover crops, often included in rotation plans, provide ground cover and stabilize the soil, preventing erosion and improving water infiltration.
The Science Behind Crop Rotation

Crop rotation is not just a random arrangement of crops; it is a well-planned strategy based on scientific principles. Here are some key scientific aspects to consider:
- Crop families: Crops can be grouped into families based on their botanical relationships. Rotating crops from different families helps to prevent the buildup of pests and diseases that specifically target certain crop families.
- Nutrient requirements: Different crops have varying nutrient demands. By rotating crops with contrasting nutrient requirements, farmers can optimize nutrient availability and minimize nutrient deficiencies.
- Soil biology: Crop rotation plays a crucial role in promoting soil biodiversity. Different crops attract and support diverse soil microorganisms, which contribute to nutrient cycling, pest control, and overall soil health.
- Crop residue management: The residue left behind after harvesting can impact subsequent crops. Proper management of crop residues, such as incorporating them into the soil or using them as mulch, can enhance soil fertility and suppress weeds.
Strategies for Effective Crop Rotation

Implementing an effective crop rotation plan requires careful consideration and planning. Here are some strategies to optimize your crop rotation:
- Diversity is key: Include a variety of crops in your rotation plan to maximize the benefits. Aim for a diverse range of crop families, nutrient requirements, and growth habits.
- Long-term planning: Develop a long-term crop rotation plan that extends beyond a single growing season. This allows for better management of soil health, pest control, and nutrient cycling.
- Crop sequencing: Pay attention to the order in which crops are grown. Certain crops can benefit from being preceded or followed by specific crops. Research and understand the ideal crop sequences for your region and soil type.
- Cover crops: Incorporate cover crops into your rotation plan. Cover crops provide numerous benefits, including soil protection, nutrient scavenging, and weed suppression. Choose cover crops that align with your goals and the specific needs of your soil.
- Crop rotation and soil testing: Regular soil testing is essential to understand the nutrient status and health of your soil. This information can guide your crop rotation decisions and help you make informed choices about nutrient management.
Crop Rotation and Sustainable Agriculture
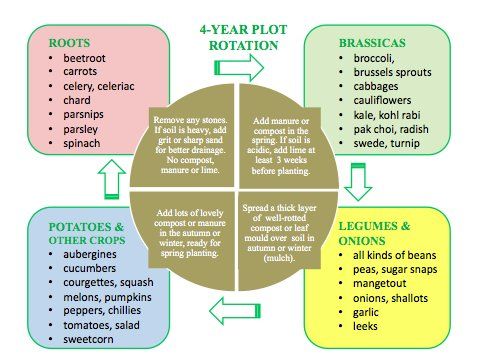
Crop rotation is a cornerstone of sustainable agriculture, offering long-term benefits for both farmers and the environment. By adopting crop rotation practices, farmers can:
- Reduce chemical inputs: Crop rotation can minimize the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides, leading to reduced environmental impact and potential cost savings.
- Promote biodiversity: Rotating crops supports biodiversity both above and below the ground. This diversity contributes to a more resilient and balanced ecosystem.
- Improve water efficiency: Properly managed crop rotations can enhance water infiltration and reduce water runoff, leading to more efficient water use and improved water quality.
- Enhance soil carbon sequestration: Certain crops, such as legumes, have the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen and increase soil organic carbon. Rotating crops with nitrogen-fixing legumes can contribute to carbon sequestration and mitigate climate change.
Challenges and Considerations

While crop rotation offers numerous advantages, there are also challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
- Market demands: Balancing crop rotation with market demands can be challenging. Some crops may have higher market value or be in higher demand, making it difficult to rotate crops optimally.
- Infrastructure and equipment: Different crops may require specific infrastructure and equipment. Ensuring that your farm has the necessary facilities and machinery to support crop rotation can be a consideration.
- Weed and pest management: While crop rotation can help manage weeds and pests, it is not a foolproof solution. Proper monitoring and timely interventions may still be necessary to control infestations.
- Soil type and climate: Different soil types and climates may require tailored crop rotation plans. Understanding your local conditions and consulting with agricultural experts can help you develop an effective rotation strategy.
Success Stories: Real-World Examples
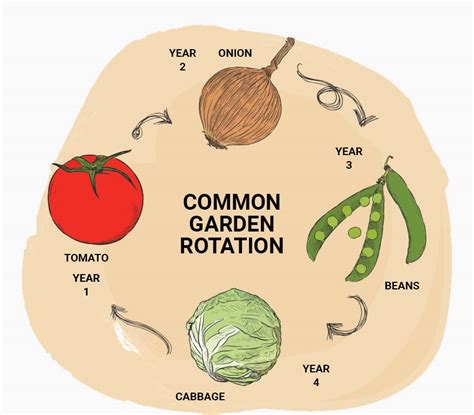
Crop rotation has proven its effectiveness through numerous success stories around the world. Here are a few examples:
- The Rodale Institute: This renowned agricultural research institute has demonstrated the benefits of crop rotation through long-term trials. Their research has shown that crop rotation can increase yields, improve soil health, and reduce the need for chemical inputs.
- The Missouri Crop Rotation Project: This project, conducted by the University of Missouri, studied the effects of crop rotation on soil health and crop productivity. The results highlighted the positive impact of crop rotation on soil organic matter, nutrient availability, and pest management.
- Organic farming success stories: Many organic farmers have successfully implemented crop rotation as a key component of their farming practices. These farmers have reported improved soil fertility, reduced pest pressure, and enhanced crop quality.
Conclusion
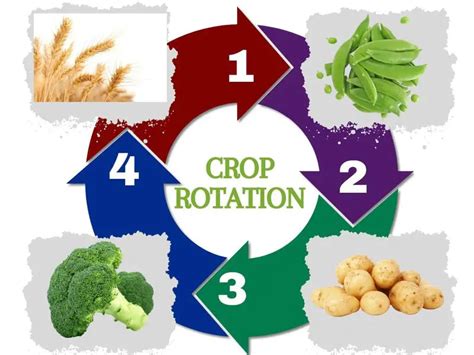
Crop rotation is a powerful tool for farmers to enhance soil health, improve crop yields, and promote sustainable agriculture. By understanding the benefits, scientific principles, and effective strategies of crop rotation, farmers can make informed decisions to optimize their agricultural practices. With careful planning and implementation, crop rotation can lead to long-term success and contribute to a more resilient and productive farming system.
What is the ideal crop rotation cycle?
+The ideal crop rotation cycle can vary depending on factors such as soil type, climate, and crop choices. However, a general guideline is to rotate crops every 2-4 years. This allows for sufficient time for soil recovery and nutrient cycling.
Can crop rotation be implemented on small-scale farms?
+Absolutely! Crop rotation is beneficial for farms of all sizes. Even small-scale farmers can implement simple crop rotation plans to improve soil health and crop productivity.
How can I choose the right crops for my rotation plan?
+When selecting crops for your rotation plan, consider factors such as crop families, nutrient requirements, and market demands. Consult with agricultural experts or extension services to develop a tailored rotation plan for your specific farm and goals.
Are there any crops that are particularly beneficial for crop rotation?
+Yes, certain crops are known for their positive impact on crop rotation. Legumes, such as beans and peas, are excellent choices as they fix atmospheric nitrogen and improve soil fertility. Cover crops, like clover or rye, can also provide numerous benefits when incorporated into the rotation plan.
What are some common mistakes to avoid in crop rotation planning?
+Some common mistakes to avoid include neglecting soil testing, not considering crop sequencing, and failing to incorporate cover crops. Additionally, it’s important to avoid over-reliance on a single crop or crop family, as this can lead to soil depletion and pest buildup.


