10 Tutorials: Unveiling The Chloroplastalgae Connection
Understanding the Chloroplast-Algae Connection: A Comprehensive Guide

The relationship between chloroplasts and algae is a fascinating one, offering insights into the intricate world of plant biology. In this blog post, we will explore ten tutorials that will help you unravel the mysteries of this connection, shedding light on the vital roles these organelles and organisms play in our ecosystem. From their evolutionary origins to their unique functions, get ready to dive into the green world of chloroplasts and algae!
Tutorial 1: The Evolution of Chloroplasts and Their Algal Ancestors

Chloroplasts, the powerhouses of plant cells, have a remarkable evolutionary story. In this tutorial, we delve into the ancient partnership between cyanobacteria and early eukaryotic cells, which led to the endosymbiotic event. We’ll explore how this symbiotic relationship gave rise to the chloroplasts we know today and how it shaped the evolution of algae and plants.
Key Takeaways:
- Chloroplasts originated from ancient cyanobacteria through endosymbiosis.
- This event occurred around 1.5 billion years ago, revolutionizing life on Earth.
- Algae, being descendants of ancient cyanobacteria, retain some of their bacterial characteristics.
- The evolution of chloroplasts and algae is a prime example of symbiotic relationships in nature.
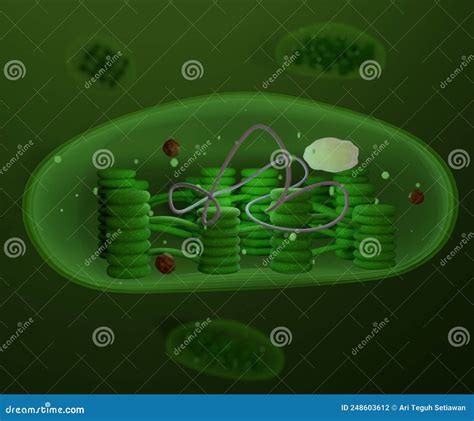
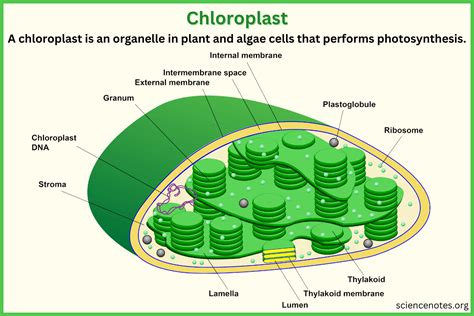
Tutorial 2: Unraveling the Structure and Function of Chloroplasts

Understanding the structure of chloroplasts is crucial to appreciating their role in photosynthesis. In this tutorial, we’ll take a closer look at the intricate organization of chloroplasts, including their thylakoid membranes, grana, and stroma. We’ll also explore the light-dependent and light-independent reactions that occur within these organelles, providing an in-depth understanding of their function.
Key Takeaways:
- Chloroplasts are double-membraned organelles with a complex internal structure.
- Thylakoid membranes house the photosynthetic pigments and are crucial for light-dependent reactions.
- Grana are stacks of thylakoid membranes, providing a platform for efficient light absorption.
- The stroma contains enzymes and other molecules necessary for the Calvin cycle (light-independent reactions).
Tutorial 3: Algae: The Diverse World of Aquatic Plants

Algae are a diverse group of photosynthetic organisms that inhabit both freshwater and marine environments. In this tutorial, we’ll explore the different types of algae, from microscopic phytoplankton to large seaweed species. We’ll also discuss their ecological importance, including their role in primary production and as a food source for various marine organisms.
Key Takeaways:
- Algae are a diverse group of photosynthetic organisms, ranging from unicellular to multicellular forms.
- They are classified into various groups based on their pigment composition and cell structure.
- Algae play a crucial role in marine ecosystems, providing food and habitat for other organisms.
- Some algae, like phytoplankton, are responsible for a significant portion of Earth’s oxygen production.
Tutorial 4: The Photosynthetic Process: A Deep Dive

Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight into chemical energy. In this tutorial, we’ll delve into the intricate steps of photosynthesis, exploring the light-dependent and light-independent reactions in detail. We’ll also discuss the role of chlorophyll and other pigments in capturing light energy and the importance of carbon dioxide and water in this process.
Key Takeaways:
- Photosynthesis is a complex process that occurs in two main stages: light-dependent and light-independent reactions.
- Light-dependent reactions take place in the thylakoid membranes, producing ATP and NADPH.
- Light-independent reactions, or the Calvin cycle, occur in the stroma, using ATP and NADPH to fix carbon dioxide into glucose.
- Chlorophyll and other pigments play a crucial role in absorbing light energy.
Tutorial 5: The Unique Adaptations of Algae for Photosynthesis
Algae have evolved unique adaptations to thrive in their aquatic environments and maximize photosynthesis. In this tutorial, we’ll explore these adaptations, including the development of specialized structures like chloroplasts and the ability to regulate their buoyancy. We’ll also discuss how algae have adapted to different light conditions and nutrient availability.
Key Takeaways:
- Algae have evolved specialized structures, such as chloroplasts, to enhance photosynthesis.
- They can regulate their buoyancy, allowing them to move towards optimal light conditions.
- Algae have adapted to low-light environments by developing efficient light-harvesting systems.
- Some algae can fix nitrogen, providing them with a unique advantage in nutrient-poor environments.
Tutorial 6: Exploring the Genetic Relationship Between Chloroplasts and Algae

The genetic relationship between chloroplasts and algae is a fascinating aspect of their connection. In this tutorial, we’ll explore how chloroplasts retain their own genetic material and how this relates to their algal origins. We’ll also discuss the concept of chloroplast DNA (cpDNA) and its role in understanding the evolutionary history of these organelles.
Key Takeaways:
- Chloroplasts have their own genetic material, known as chloroplast DNA (cpDNA).
- cpDNA is inherited from their algal ancestors and has a circular structure.
- The study of cpDNA provides insights into the evolutionary relationships between different groups of algae and plants.
- Chloroplasts and algae share similar genetic codes, further highlighting their close connection.
Tutorial 7: The Role of Chloroplasts in Plant Development and Growth

Chloroplasts are not only involved in photosynthesis but also play a crucial role in plant development and growth. In this tutorial, we’ll explore how chloroplasts contribute to cell division, differentiation, and the overall architecture of plants. We’ll also discuss the signaling pathways between chloroplasts and the nucleus, which are essential for plant growth and adaptation.
Key Takeaways:
- Chloroplasts are involved in various aspects of plant development, including cell division and differentiation.
- They produce signaling molecules that regulate gene expression in the nucleus, influencing plant growth and development.
- Chloroplasts contribute to the formation of plant organs, such as leaves and roots.
- The communication between chloroplasts and the nucleus is vital for plants to respond to environmental cues.
Tutorial 8: Algal Blooms: Causes, Impacts, and Management

Algal blooms are a natural phenomenon, but they can have significant environmental and economic impacts. In this tutorial, we’ll explore the causes of algal blooms, including nutrient pollution and favorable environmental conditions. We’ll also discuss the impacts of these blooms on aquatic ecosystems and human activities, as well as strategies for managing and mitigating their effects.
Key Takeaways:
- Algal blooms occur when certain conditions, such as nutrient pollution and sunlight, favor the rapid growth of algae.
- These blooms can have detrimental effects on aquatic ecosystems, leading to oxygen depletion and the death of other organisms.
- Human activities, such as agriculture and wastewater discharge, can contribute to the occurrence of algal blooms.
- Management strategies include reducing nutrient pollution, improving water circulation, and using biological control methods.
Tutorial 9: The Importance of Chloroplasts in Human Health and Nutrition

Chloroplasts and algae have significant implications for human health and nutrition. In this tutorial, we’ll explore how algae are used as a source of food and supplements, providing essential nutrients and potential health benefits. We’ll also discuss the role of chloroplasts in producing valuable compounds, such as antioxidants and pharmaceuticals.
Key Takeaways:
- Algae are a rich source of nutrients, including proteins, vitamins, and minerals.
- They are used in various food products and supplements, promoting a healthy diet.
- Chloroplasts produce valuable compounds with potential medicinal properties, such as antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents.
- Research is ongoing to explore the full potential of chloroplasts and algae in healthcare and nutrition.
Tutorial 10: The Future of Chloroplast-Algae Research and Applications
The study of chloroplasts and algae continues to advance, offering exciting possibilities for various fields. In this tutorial, we’ll discuss the future directions of chloroplast-algae research, including the development of biofuels, the improvement of crop productivity, and the exploration of new pharmaceutical compounds. We’ll also explore the potential applications of this research in addressing global challenges.
Key Takeaways:
- Chloroplast-algae research has the potential to revolutionize biofuel production, offering a sustainable energy source.
- Improving our understanding of chloroplasts can lead to enhanced crop productivity and resilience.
- The development of new pharmaceutical compounds from chloroplasts and algae holds promise for treating various diseases.
- This research can contribute to sustainable agriculture, environmental conservation, and human health.
Notes:
📌 Note: The tutorials provided offer a comprehensive overview of the chloroplast-algae connection. Further exploration and research can uncover even more fascinating aspects of this relationship.
Final Thoughts
By delving into these ten tutorials, we hope you’ve gained a deeper understanding of the intricate relationship between chloroplasts and algae. From their evolutionary origins to their impact on human health and the environment, these organelles and organisms continue to captivate and inspire scientists and enthusiasts alike. The chloroplast-algae connection is a testament to the beauty and complexity of life on Earth, and further research will undoubtedly reveal even more astonishing discoveries.
FAQ
What is the primary function of chloroplasts in plants and algae?
+Chloroplasts are primarily responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert sunlight into chemical energy. This energy is then used to power various cellular processes and support the growth and development of the organism.
How do chloroplasts contribute to the evolution of plants and algae?
+Chloroplasts played a crucial role in the evolution of plants and algae by enabling these organisms to harness sunlight as an energy source. This evolutionary advantage allowed them to thrive and diversify, leading to the development of complex ecosystems and the dominance of land plants on Earth.
What are some practical applications of chloroplast-algae research?
+Chloroplast-algae research has a wide range of practical applications, including the development of sustainable biofuels, the improvement of crop productivity and resilience, and the discovery of new pharmaceutical compounds. Additionally, algae-based products and supplements offer a nutritious and sustainable food source.
How can I learn more about the chloroplast-algae connection?
+To delve deeper into the chloroplast-algae connection, you can explore scientific research papers, attend conferences and workshops, and engage with experts in the field. Additionally, online resources and educational platforms can provide valuable insights and tutorials on this fascinating topic.
What are some challenges and controversies surrounding chloroplast-algae research?
+While chloroplast-algae research offers tremendous potential, it also faces challenges and controversies. Some of these include the environmental impact of large-scale algal cultivation, the ethical considerations of genetic modification, and the need for further research to fully understand the long-term effects of certain applications.
