1. Ultimate Guide: 10 Pro Tips For Efficient Heat Exchanger Design

Introduction to Heat Exchanger Design

Heat exchangers are vital components in various industries, from HVAC systems to chemical processing. Designing an efficient heat exchanger is crucial for optimal performance and energy savings. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore ten expert tips to enhance your heat exchanger design process, ensuring maximum efficiency and effectiveness. By following these tips, you can create heat exchangers that meet the demands of your specific applications while minimizing energy consumption and operational costs.
Understanding the Basics of Heat Exchangers

Before delving into the design process, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental principles of heat exchangers. Heat exchangers facilitate the transfer of thermal energy between two or more fluids, either directly or indirectly. They are designed to maximize heat transfer while minimizing the size and cost of the system. There are several types of heat exchangers, including shell and tube, plate, and air-cooled exchangers, each with its own advantages and applications.
Tip 1: Define Your Heat Exchanger Objectives
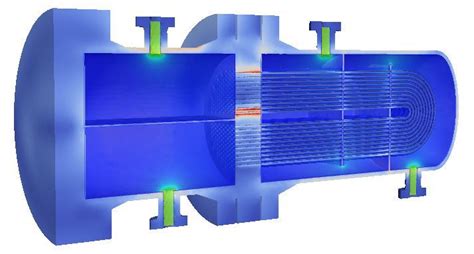
The first step in efficient heat exchanger design is to clearly define your objectives. Consider the specific requirements of your application, such as the desired heat transfer rate, temperature limits, fluid properties, and space constraints. By setting well-defined objectives, you can tailor your design to meet these requirements and optimize the performance of your heat exchanger.
Tip 2: Select the Right Heat Exchanger Type

Choosing the appropriate heat exchanger type is crucial for achieving optimal performance. Consider factors such as the nature of the fluids involved, the desired heat transfer rate, and the available space. Shell and tube exchangers are suitable for high-pressure applications, while plate exchangers offer compactness and efficiency. Air-cooled exchangers are ideal for outdoor installations or situations where water is scarce. Evaluate your specific needs and select the heat exchanger type that best aligns with your objectives.
Tip 3: Optimize Fluid Flow Patterns

Efficient fluid flow is essential for effective heat transfer. Optimize the flow patterns within your heat exchanger by considering factors such as fluid viscosity, velocity, and turbulence. Aim for uniform flow distribution and minimize flow restrictions to ensure optimal heat transfer. Consider using flow-enhancing devices such as baffles or fins to improve the flow patterns and enhance heat transfer efficiency.
Tip 4: Choose the Right Materials

The selection of appropriate materials is critical for the durability and performance of your heat exchanger. Consider the compatibility of the materials with the fluids being used, as well as the operating conditions, such as temperature and pressure. Common materials used in heat exchangers include stainless steel, copper, and aluminum. Select materials that offer the necessary corrosion resistance, strength, and thermal conductivity to ensure the long-term reliability of your heat exchanger.
Tip 5: Optimize Heat Transfer Surface Area
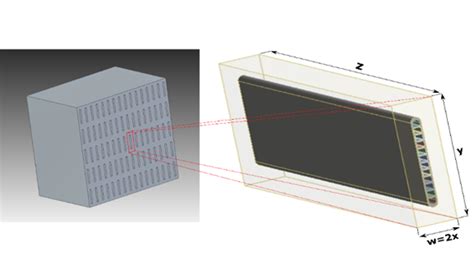
Maximizing the heat transfer surface area is crucial for efficient heat exchanger design. Increase the surface area by incorporating features such as fins, grooves, or enhanced surfaces. These enhancements provide additional contact points for heat transfer, improving the overall efficiency of the exchanger. Calculate the required surface area based on your heat transfer requirements and select an appropriate design that optimizes this parameter.
Tip 6: Minimize Pressure Drop
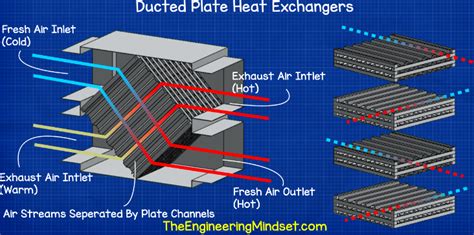
Reducing pressure drop is essential for maintaining efficient fluid flow and minimizing energy consumption. Design your heat exchanger with low-pressure drop in mind. Consider factors such as fluid viscosity, flow rate, and the complexity of the flow path. Optimize the flow path by minimizing sharp turns and restrictions, and ensure that the exchanger is properly sized to handle the required flow rates without excessive pressure loss.
Tip 7: Incorporate Effective Insulation

Proper insulation is crucial for preventing heat loss and maintaining the desired temperature conditions. Insulate your heat exchanger to minimize heat transfer to the surroundings and maximize the efficiency of the system. Select insulation materials with low thermal conductivity and ensure they are properly installed to avoid gaps or air pockets. Regularly inspect and maintain the insulation to prevent degradation over time.
Tip 8: Consider Maintenance and Cleaning

Designing a heat exchanger with ease of maintenance and cleaning in mind is essential for long-term performance. Incorporate features such as removable covers, access panels, or clean-in-place (CIP) systems to facilitate regular maintenance and cleaning. Ensure that the design allows for efficient removal of fouling or scaling, which can impact heat transfer efficiency. Regular maintenance and cleaning will help extend the lifespan of your heat exchanger and maintain optimal performance.
Tip 9: Use Simulation and Modeling Tools
Utilizing simulation and modeling tools can greatly enhance the design process and optimize the performance of your heat exchanger. These tools allow you to simulate various operating conditions, evaluate different design configurations, and predict the heat transfer performance. By running simulations, you can identify potential issues, optimize design parameters, and make informed decisions to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of your heat exchanger.
Tip 10: Conduct Regular Performance Evaluations
Even after the initial design and installation, it’s crucial to conduct regular performance evaluations to ensure the heat exchanger is operating efficiently. Monitor key parameters such as temperature, pressure, and flow rates to identify any deviations from the expected performance. Regular performance evaluations allow you to detect and address any issues promptly, ensuring the long-term reliability and efficiency of your heat exchanger.
Conclusion
Efficient heat exchanger design is a multifaceted process that requires careful consideration of various factors. By following these ten expert tips, you can optimize your heat exchanger design, enhance its performance, and achieve energy savings. From defining clear objectives to selecting the right materials and incorporating effective insulation, each step plays a crucial role in the overall efficiency and effectiveness of your heat exchanger. Remember to regularly evaluate and maintain your heat exchanger to ensure its optimal performance over its lifespan.
FAQ
What are the common applications of heat exchangers?
+Heat exchangers have a wide range of applications, including HVAC systems, refrigeration, chemical processing, power generation, and waste heat recovery.
How can I calculate the required heat transfer surface area for my heat exchanger?
+The required heat transfer surface area can be calculated using heat transfer equations, considering factors such as the desired heat transfer rate, fluid properties, and temperature difference.
What are some common issues that can affect heat exchanger performance?
+Common issues include fouling, scaling, corrosion, and improper maintenance. Regular cleaning, proper insulation, and regular performance evaluations can help mitigate these issues.
Can I use simulation tools for heat exchanger design without any prior experience?
+While simulation tools can be powerful, they require a certain level of expertise. It is recommended to seek guidance or training to effectively utilize these tools for heat exchanger design.
How often should I conduct performance evaluations for my heat exchanger?
+The frequency of performance evaluations depends on the specific application and operating conditions. As a general guideline, it is recommended to conduct evaluations at regular intervals, such as quarterly or biannually, to ensure optimal performance.