1. Design Your Decimal: 5 Ultimate Steps

Designing your own decimal system might seem like a daunting task, but with these five ultimate steps, you'll be on your way to creating a unique and functional numerical representation. Let's dive in and explore the world of decimals!
Step 1: Understand the Basics

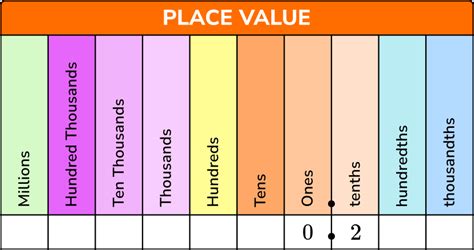
Before we begin, let's familiarize ourselves with the fundamental concepts of decimals. A decimal, or a base-10 number system, is a way of representing numbers using ten unique digits (0-9) and a radix point (or decimal point) to separate the whole number part from the fractional part.
In a decimal system, each digit position represents a power of ten. For example, in the number 345.67, the 3 is in the hundreds place (102), the 4 is in the tens place (101), the 5 is in the ones place (100), the .67 represents the tenths and hundredths places (10-1 and 10-2 respectively), and so on.
Step 2: Choose Your Radix

The radix, or base, of a number system, determines the number of unique digits used. In our familiar decimal system, the radix is 10, giving us the digits 0-9. However, when designing your own decimal system, you have the freedom to choose a different radix.
Some common radix choices include:
- Binary (Base 2): Uses only two digits (0 and 1), commonly used in computer science.
- Octal (Base 8): Utilizes eight digits (0-7), often used in computing for representing file permissions.
- Hexadecimal (Base 16): Employs sixteen digits (0-9 and A-F or 0-9 and a-f), popular in programming and web development.
When selecting your radix, consider the purpose of your decimal system and the range of numbers you need to represent. A higher radix allows for more unique digits and a larger range of numbers, but it may also make calculations more complex.
Step 3: Determine Your Digits

Once you've chosen your radix, it's time to decide on the digits that will make up your decimal system. If you're working with a small radix, like binary or octal, you may simply use the digits 0 and 1 or 0-7 respectively.
For larger radices, like hexadecimal or your custom decimal system, you'll need to create a set of unique digits or symbols to represent each position. You can use letters, special characters, or even pictures to represent these digits. Get creative and have fun with it!
For example, let's say we're designing a decimal system with a radix of 12. We could use the digits 0-9, and then assign specific symbols or letters to represent the remaining two digits. Perhaps we choose the letter A for the number 10 and the letter B for the number 11.
Step 4: Create a Conversion Chart
To ensure consistency and ease of use, create a conversion chart that translates your new decimal system into the familiar base-10 system. This chart will help you and others quickly understand the relationship between your custom decimal numbers and their base-10 equivalents.
For instance, let's continue with our example of a decimal system with a radix of 12. Our conversion chart might look something like this:
| Decimal (Base 12) | Base 10 Equivalent |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 |
| ... | ... |
| A | 10 |
| B | 11 |
| 10 | 12 |
| 11 | 13 |
| ... | ... |

This chart allows us to quickly convert between our custom decimal system and the base-10 system, making calculations and comparisons easier.
Step 5: Practice and Refine

Now that you have the basic framework of your decimal system, it's time to put it into practice. Start by performing simple calculations and conversions using your new system. As you work with it, you may discover areas where your system could be improved or refined.
For example, you might find that certain digits or symbols are confusing or difficult to work with. In these cases, you can go back and make adjustments to your digit choices or even consider changing your radix if necessary.
Remember, designing a decimal system is an iterative process, and it may take some time and experimentation to find the perfect balance between functionality and ease of use.
Conclusion

Designing your own decimal system is an exciting and creative endeavor. By following these five steps, you can create a unique and personalized way of representing numbers. Whether you're a mathematician, a programmer, or simply someone with an interest in numerical systems, designing your decimal offers a fun and engaging way to explore the world of mathematics.
Frequently Asked Questions

Can I use non-standard digits or symbols in my decimal system?
+Absolutely! One of the benefits of designing your own decimal system is the freedom to choose unique digits or symbols. You can use letters, special characters, or even pictures to represent your digits. Just ensure that your choices are consistent and easy to understand.
How do I perform calculations in my custom decimal system?
+Calculations in your custom decimal system follow the same principles as any other number system. You can use standard arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Just remember to convert your numbers to base-10 for more complex calculations if needed.
Can I use my custom decimal system for practical applications?
+Certainly! While designing a custom decimal system might seem like a theoretical exercise, it can have practical applications. For example, you could use your system for internal coding or labeling within your organization, or even as a fun way to represent data in a unique and memorable way.
Is there a limit to the radix I can choose for my decimal system?
+In theory, there is no limit to the radix you can choose. However, it’s important to consider the practicality and ease of use. Very large radices may result in long and complex numbers, making calculations and conversions more challenging. Strike a balance between the range of numbers you need to represent and the simplicity of your system.
